Climate Metrics from daily weather data
The R Script associated with this page is available here. Download this file and open it (or copy-paste into a new script) with RStudio so you can follow along.
Summary
- Access and work with station weather data from Global Historical Climate Network (GHCN)
- Explore options for plotting timeseries
- Trend analysis
- Compute Climate Extremes
Climate Metrics
Climate Metrics: ClimdEX
Indices representing extreme aspects of climate derived from daily data:
Climate Change Research Centre (CCRC) at University of New South Wales (UNSW) (climdex.org).
27 Core indices
For example:
- FD Number of frost days: Annual count of days when TN (daily minimum temperature) < 0C.
- SU Number of summer days: Annual count of days when TX (daily maximum temperature) > 25C.
- ID Number of icing days: Annual count of days when TX (daily maximum temperature) < 0C.
- TR Number of tropical nights: Annual count of days when TN (daily minimum temperature) > 20C.
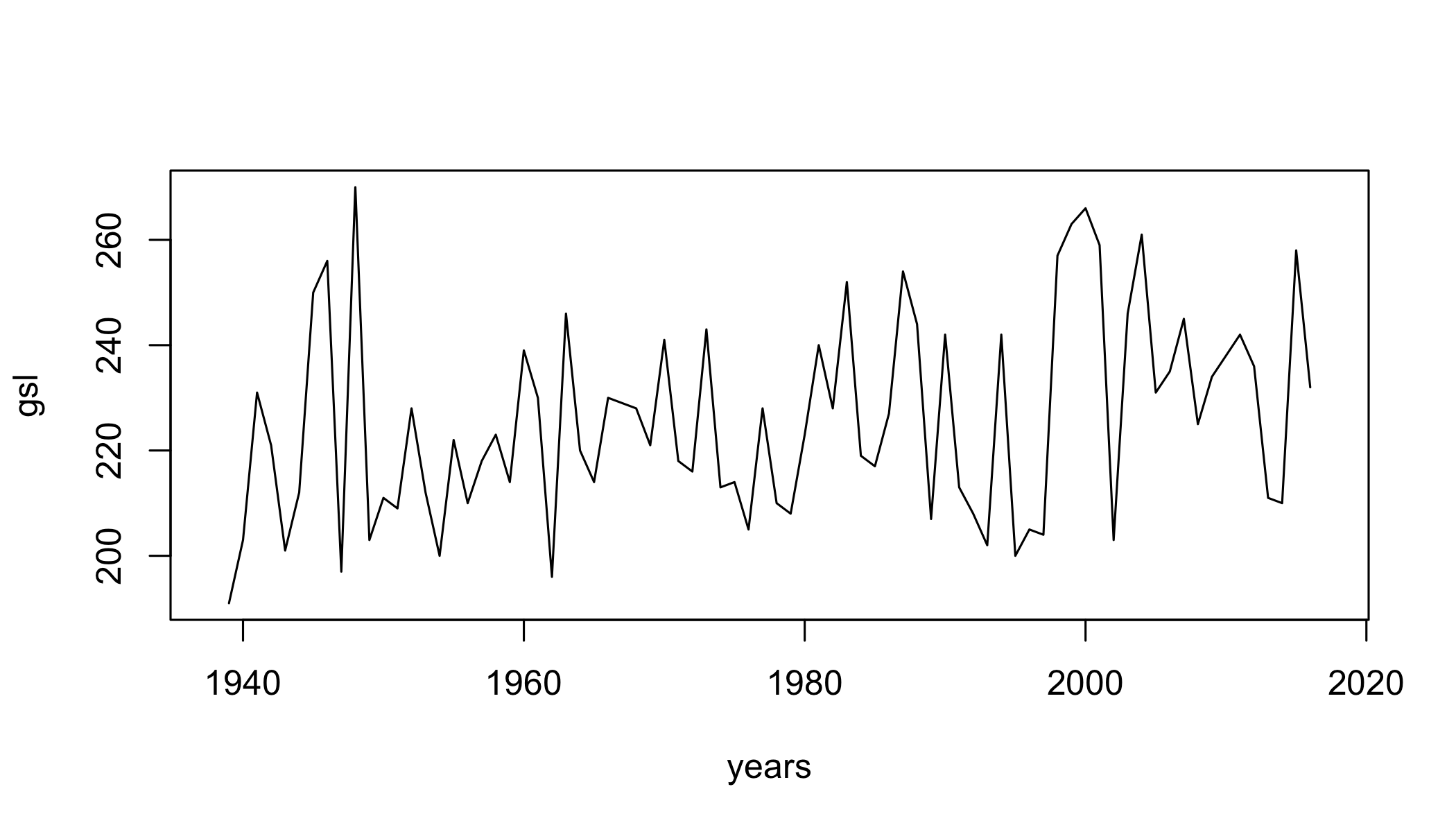
- GSL Growing season length: Annual (1st Jan to 31st Dec in Northern Hemisphere (NH), 1st July to 30th June in Southern Hemisphere (SH)) count between first span of at least 6 days with daily mean temperature TG>5C and first span after July 1st (Jan 1st in SH) of 6 days with TG<5C.
- TXx Monthly maximum value of daily maximum temperature
- TN10p Percentage of days when TN < 10th percentile
- Rx5day Monthly maximum consecutive 5-day precipitation
- SDII Simple pricipitation intensity index
Weather Data
Climate Data Online
CDO
GHCN

ghcn
Options for downloading data
FedData package
- National Elevation Dataset digital elevation models (1 and 1/3 arc-second; USGS)
- National Hydrography Dataset (USGS)
- Soil Survey Geographic (SSURGO) database
- International Tree Ring Data Bank.
- Global Historical Climatology Network (GHCN)
rNOAA package
Handles downloading data directly from NOAA APIv2.
buoy_*NOAA Buoy data from the National Buoy Data Centerghcnd_*GHCND daily data from NOAAisd_*ISD/ISH data from NOAAhomr_*Historical Observing Metadata Repositoryncdc_*NOAA National Climatic Data Center (NCDC)seaiceSea icestorm_Storms (IBTrACS)swdiSevere Weather Data Inventory (SWDI)tornadoesFrom the NOAA Storm Prediction Center
Libraries
library(raster)
library(sp)
library(rgdal)
library(ggplot2)
library(ggmap)
library(dplyr)
library(tidyr)
library(maps)
library(scales)
# New Packages
library(rnoaa)
library(climdex.pcic)
library(zoo)
library(reshape2)
library(broom)Station locations
Download the GHCN station inventory with ghcnd_stations().
datadir="data"
st = ghcnd_stations()
## Optionally, save it to disk
# write.csv(st,file.path(datadir,"st.csv"))
## If internet fails, load the file from disk using:
# st=read.csv(file.path(datadir,"st.csv"))GHCND Variables
5 core values:
- PRCP Precipitation (tenths of mm)
- SNOW Snowfall (mm)
- SNWD Snow depth (mm)
- TMAX Maximum temperature
- TMIN Minimum temperature
And ~50 others! For example:
- ACMC Average cloudiness midnight to midnight from 30-second ceilometer
- AWND Average daily wind speed
- FMTM Time of fastest mile or fastest 1-minute wind
- MDSF Multiday snowfall total
filter() to temperature and precipitation
st=dplyr::filter(st,element%in%c("TMAX","TMIN","PRCP"))Map GHCND stations
First, get a global country polygon
worldmap=map_data("world")Plot all stations:
ggplot(data=st,aes(y=latitude,x=longitude)) +
facet_grid(element~.)+
annotation_map(map=worldmap,size=.1,fill="grey",colour="black")+
geom_point(size=.1,col="red")+
coord_equal()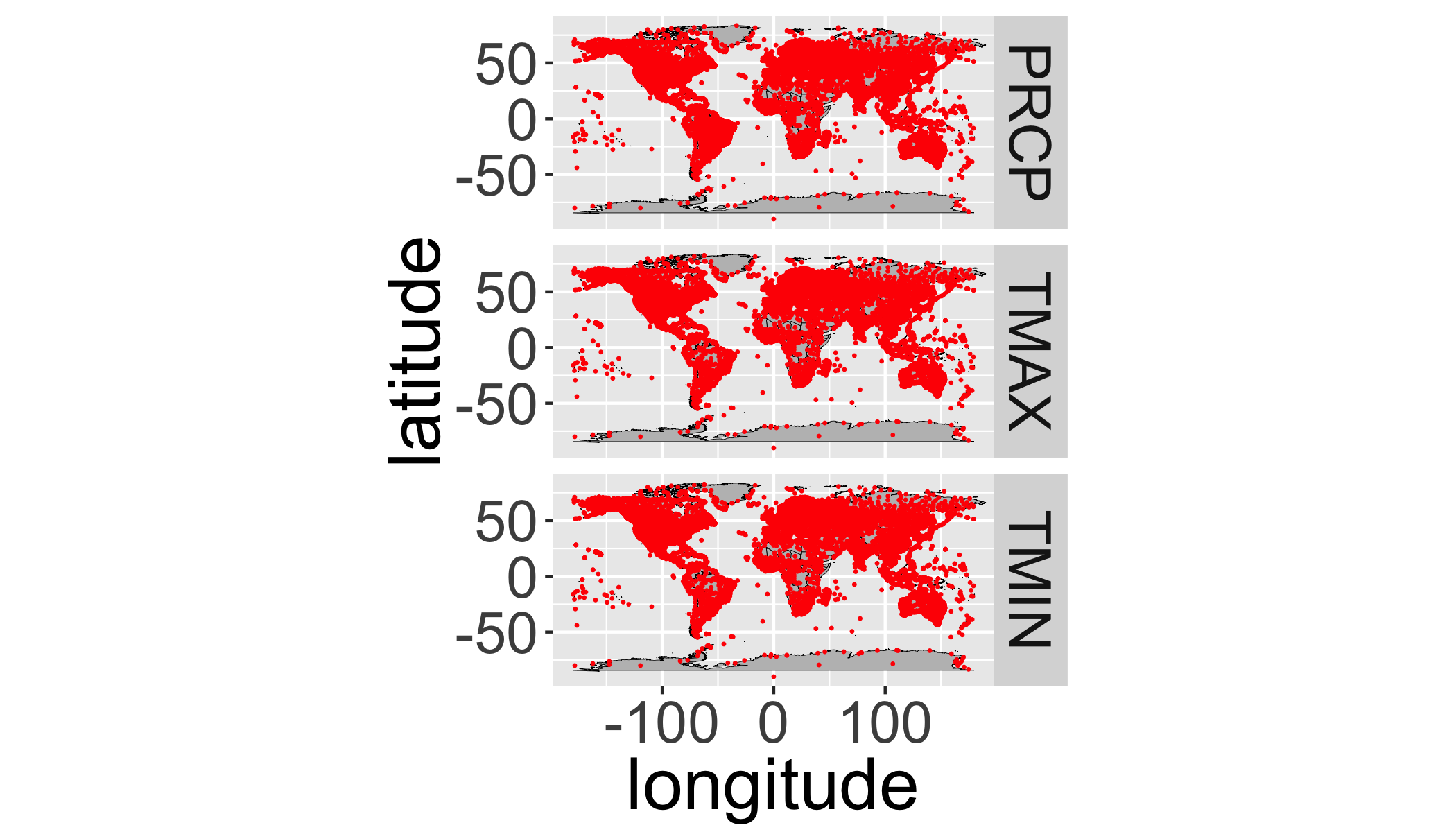
It’s hard to see all the points, let’s bin them…
ggplot(st,aes(y=latitude,x=longitude)) +
annotation_map(map=worldmap,size=.1,fill="grey",colour="black")+
facet_grid(element~.)+
stat_bin2d(bins=100)+
scale_fill_distiller(palette="YlOrRd",trans="log",direction=-1,
breaks = c(1,10,100,1000))+
coord_equal()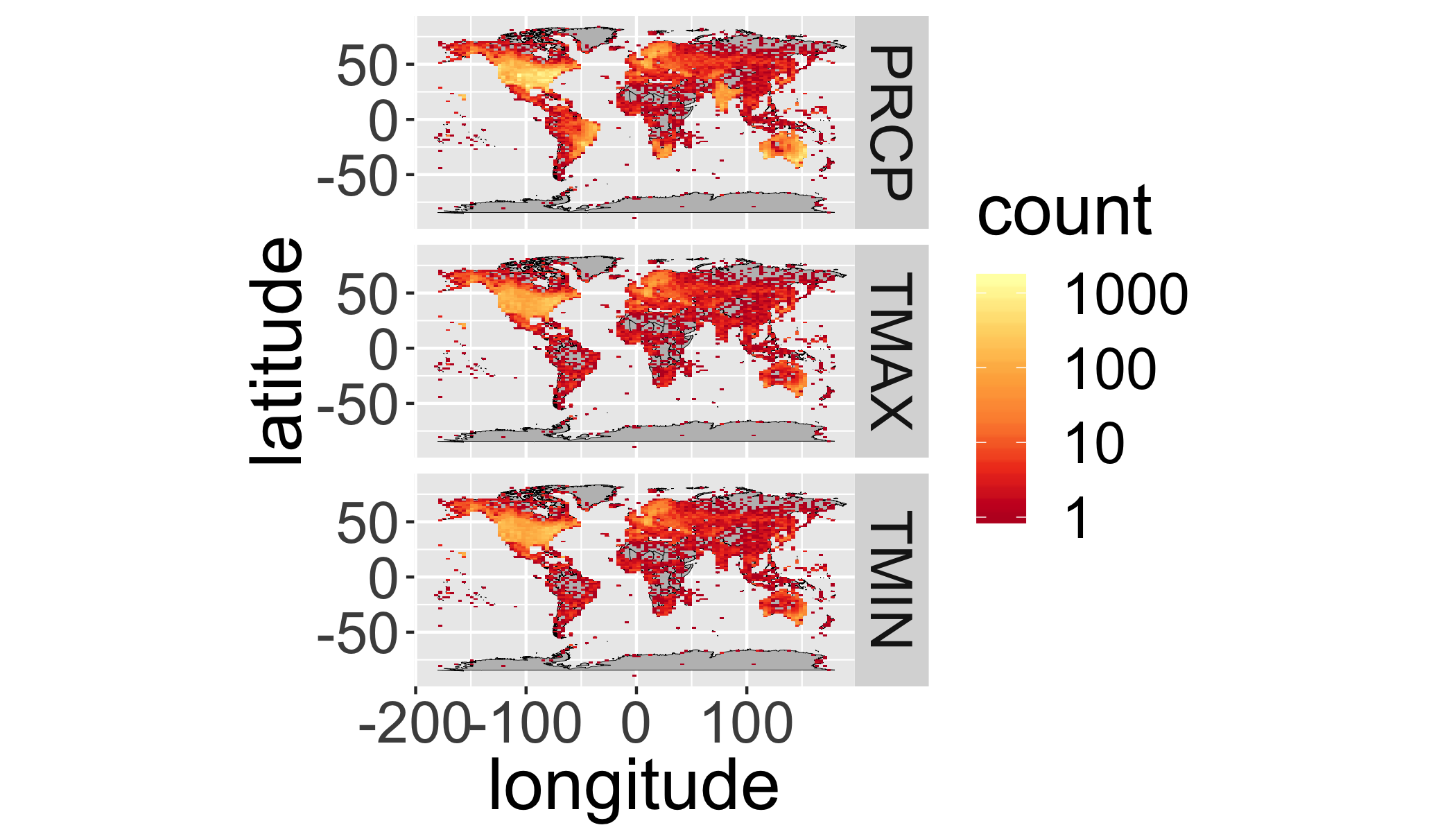
Your turn
Produce a binned map (like above) with the following modifications:
- include only stations with a data record that starts before 1950 and ends after 2000 (keeping only complete records during that time).
- include only
tmax
ggplot(filter(st,
first_year<=1950 &
last_year>=2000 &
element=="TMAX"),
aes(y=latitude,x=longitude)) +
annotation_map(map=worldmap,size=.1,fill="grey",colour="black")+
stat_bin2d(bins=75)+
scale_fill_distiller(palette="YlOrRd",trans="log",direction=-1,
breaks = c(1,10,50))+
coord_equal()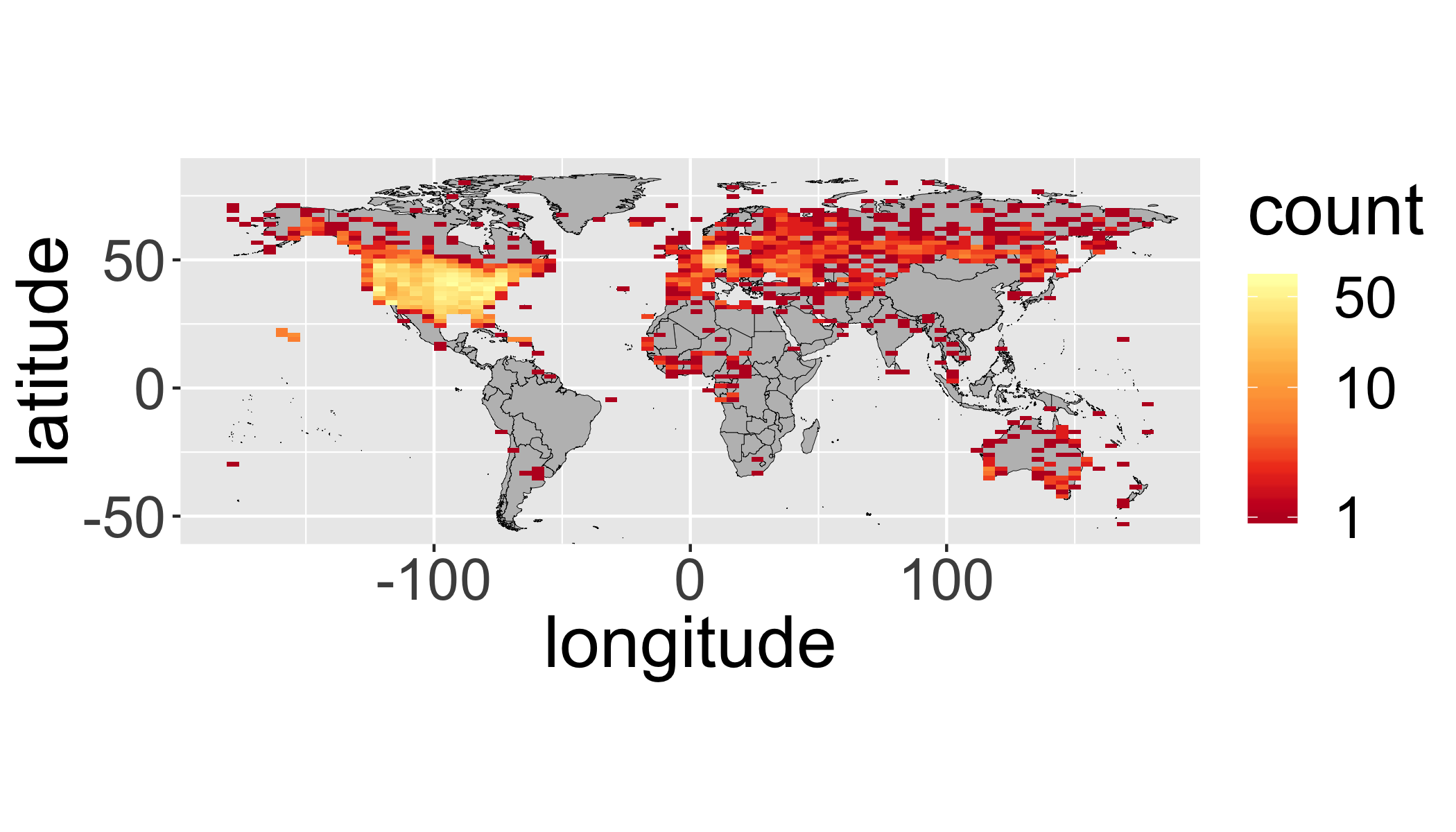
Download daily data from GHCN
ghcnd() will download a .dly file for a particular station. But how to choose?
geocode in ggmap package useful for geocoding place names
Geocodes a location (find latitude and longitude) using either (1) the Data Science Toolkit (http://www.datasciencetoolkit.org/about) or (2) Google Maps.
geocode("University at Buffalo, NY")## Source : https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/geocode/json?address=University%20at%20Buffalo%2C%20NY## lon lat
## 1 -78.78897 43.00081However, you have to be careful:
geocode("My Grandma's house")## Source : https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/geocode/json?address=My%20Grandma%27s%20house## lon lat
## 1 -97.18744 32.82241But this is pretty safe for well known places.
coords=as.matrix(geocode("Buffalo, NY"))## Source : https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/geocode/json?address=Buffalo%2C%20NYcoords## lon lat
## [1,] -78.87837 42.88645Now use that location to spatially filter stations with a rectangular box.
dplyr::filter(st,
grepl("BUFFALO",name)&
between(latitude,coords[2]-1,coords[2]+1) &
between(longitude,coords[1]-1,coords[1]+1)&
element=="TMAX")## # A tibble: 3 x 11
## id latitude longitude elevation state name gsn_flag wmo_id element
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
## 1 USC0… 42.9 -78.9 -1000. NY BUFF… "" "" TMAX
## 2 USC0… 42.9 -78.9 177. NY BUFF… "" "" TMAX
## 3 USW0… 42.9 -78.7 211. NY BUFF… "" HCN 7… TMAX
## # ... with 2 more variables: first_year <int>, last_year <int>You could also spatially filter using over() in sp package…
With the station ID, we can now download daily data from NOAA.
d=meteo_tidy_ghcnd("USW00014733",
var = c("TMAX","TMIN","PRCP"),
keep_flags=T)
head(d)## # A tibble: 6 x 14
## id date mflag_prcp mflag_tmax mflag_tmin prcp qflag_prcp
## <chr> <date> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <chr>
## 1 USW0… 1938-05-01 T " " " " 0 " "
## 2 USW0… 1938-05-02 T " " " " 0 " "
## 3 USW0… 1938-05-03 " " " " " " 25 " "
## 4 USW0… 1938-05-04 " " " " " " 112 " "
## 5 USW0… 1938-05-05 T " " " " 0 " "
## 6 USW0… 1938-05-06 " " " " " " 64 " "
## # ... with 7 more variables: qflag_tmax <chr>, qflag_tmin <chr>,
## # sflag_prcp <chr>, sflag_tmax <chr>, sflag_tmin <chr>, tmax <dbl>,
## # tmin <dbl>See CDO Daily Description and raw GHCND metadata for more details. If you want to download multiple stations at once, check out meteo_pull_monitors()
Quality Control: MFLAG
Measurement Flag/Attribute
- Blank no measurement information applicable
- B precipitation total formed from two twelve-hour totals
- H represents highest or lowest hourly temperature (TMAX or TMIN) or average of hourly values (TAVG)
- K converted from knots
- …
See CDO Description
Quality Control: QFLAG
- Blank did not fail any quality assurance check
- D failed duplicate check
- G failed gap check
- K failed streak/frequent-value check
- N failed naught check
- O failed climatological outlier check
- S failed spatial consistency check
- T failed temporal consistency check
- W temperature too warm for snow
- …
See CDO Description
Quality Control: SFLAG
Indicates the source of the data…
Summarize QC flags
Summarize the QC flags. How many of which type are there? Should we be more conservative?
table(d$qflag_tmax) ##
## G I
## 29027 2 10table(d$qflag_tmin) ##
## G I S
## 29026 2 7 4table(d$qflag_prcp) ##
## G
## 29038 1- T failed temporal consistency check
Filter with QC data and change units
d_filtered=d%>%
mutate(tmax=ifelse(qflag_tmax!=" "|tmax==-9999,NA,tmax/10))%>% # convert to degrees C
mutate(tmin=ifelse(qflag_tmin!=" "|tmin==-9999,NA,tmin/10))%>% # convert to degrees C
mutate(prcp=ifelse(qflag_tmin!=" "|prcp==-9999,NA,prcp))%>% # convert to degrees C
arrange(date)Plot temperatures
ggplot(d_filtered,
aes(y=tmax,x=date))+
geom_line(col="red")## Warning: Removed 11 rows containing missing values (geom_path).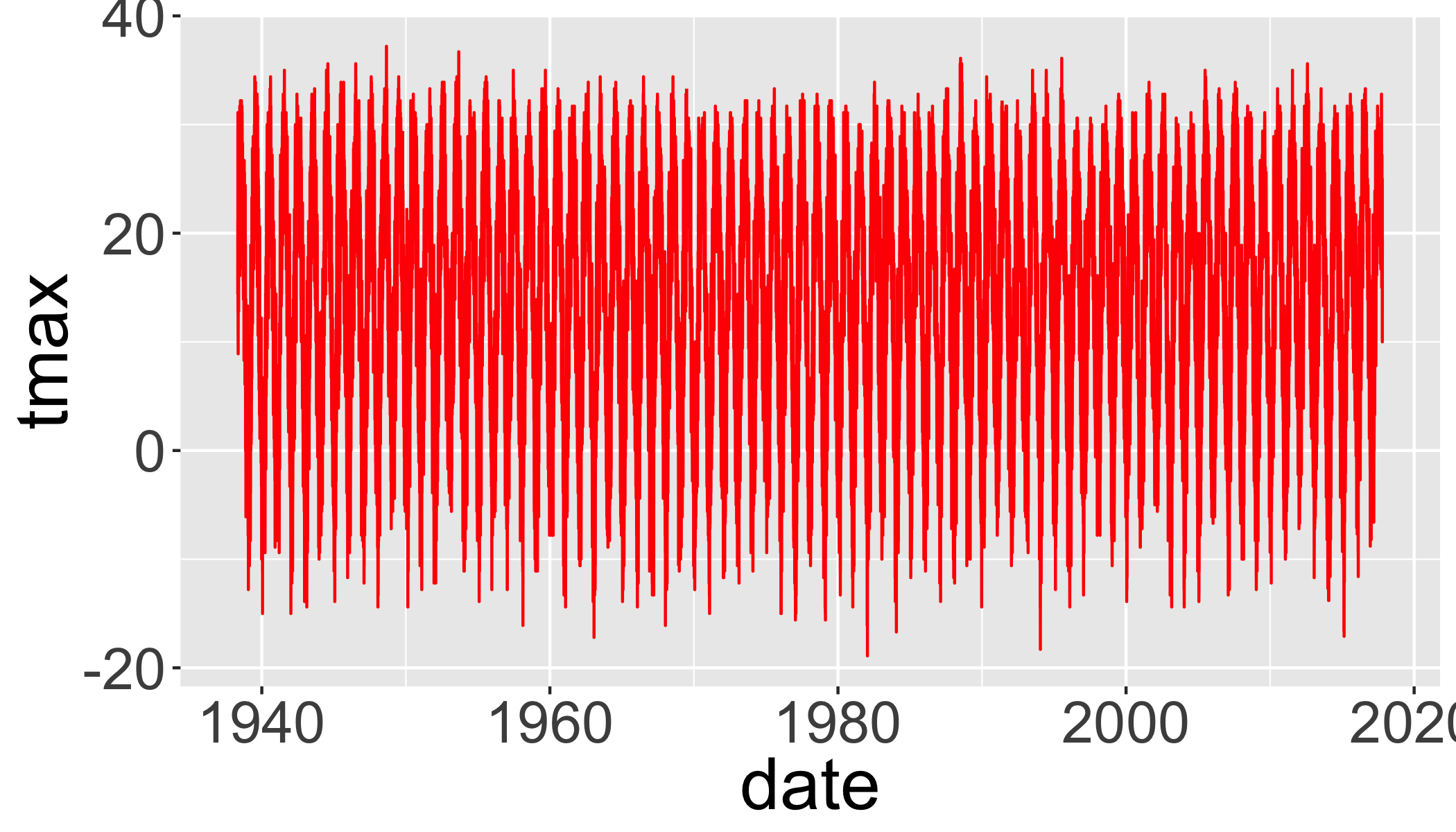
Limit to a few years and plot the daily range and average temperatures.
d_filtered_recent=filter(d_filtered,date>as.Date("2013-01-01"))
ggplot(d_filtered_recent,
aes(ymax=tmax,ymin=tmin,x=date))+
geom_ribbon(col="grey",fill="grey")+
geom_line(aes(y=(tmax+tmin)/2),col="red")## Warning: Removed 11 rows containing missing values (geom_path).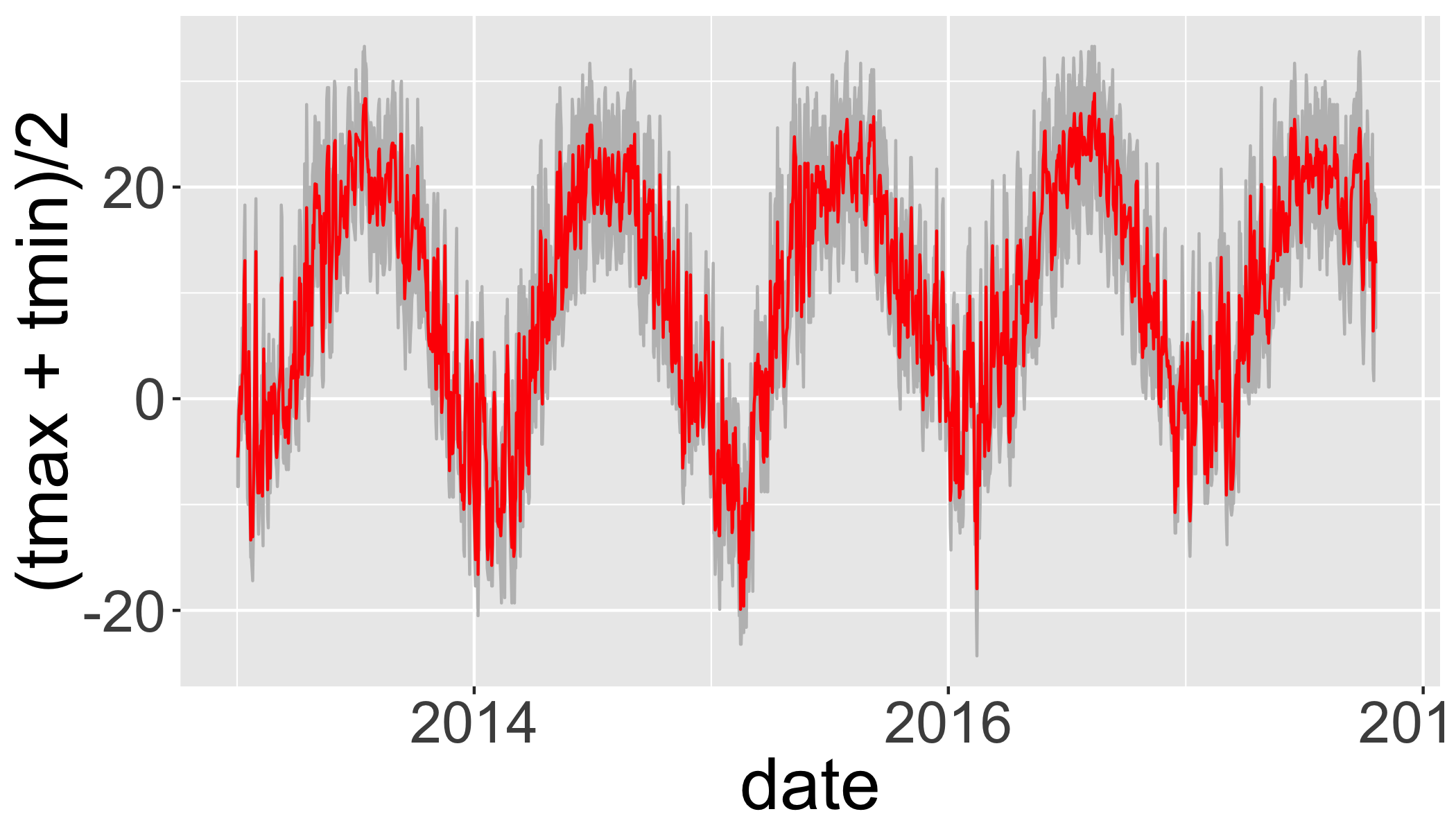
Zoo package for rolling functions
Infrastructure for Regular and Irregular Time Series (Z’s Ordered Observations)
rollmean(): Rolling meanrollsum(): Rolling sumrollapply(): Custom functions
Use rollmean to calculate a rolling 60-day average.
alignwhether the index of the result should be left- or right-aligned or centered
d_rollmean = d_filtered_recent %>%
arrange(date) %>%
mutate(tmax.60 = rollmean(x = tmax, 60, align = "center", fill = NA),
tmax.b60 = rollmean(x = tmax, 60, align = "right", fill = NA))d_rollmean%>%
ggplot(aes(ymax=tmax,ymin=tmin,x=date))+
geom_ribbon(fill="grey")+
geom_line(aes(y=(tmin+tmax)/2),col=grey(0.4),size=.5)+
geom_line(aes(y=tmax.60),col="red")+
geom_line(aes(y=tmax.b60),col="darkred")## Warning: Removed 11 rows containing missing values (geom_path).## Warning: Removed 70 rows containing missing values (geom_path).
## Warning: Removed 70 rows containing missing values (geom_path).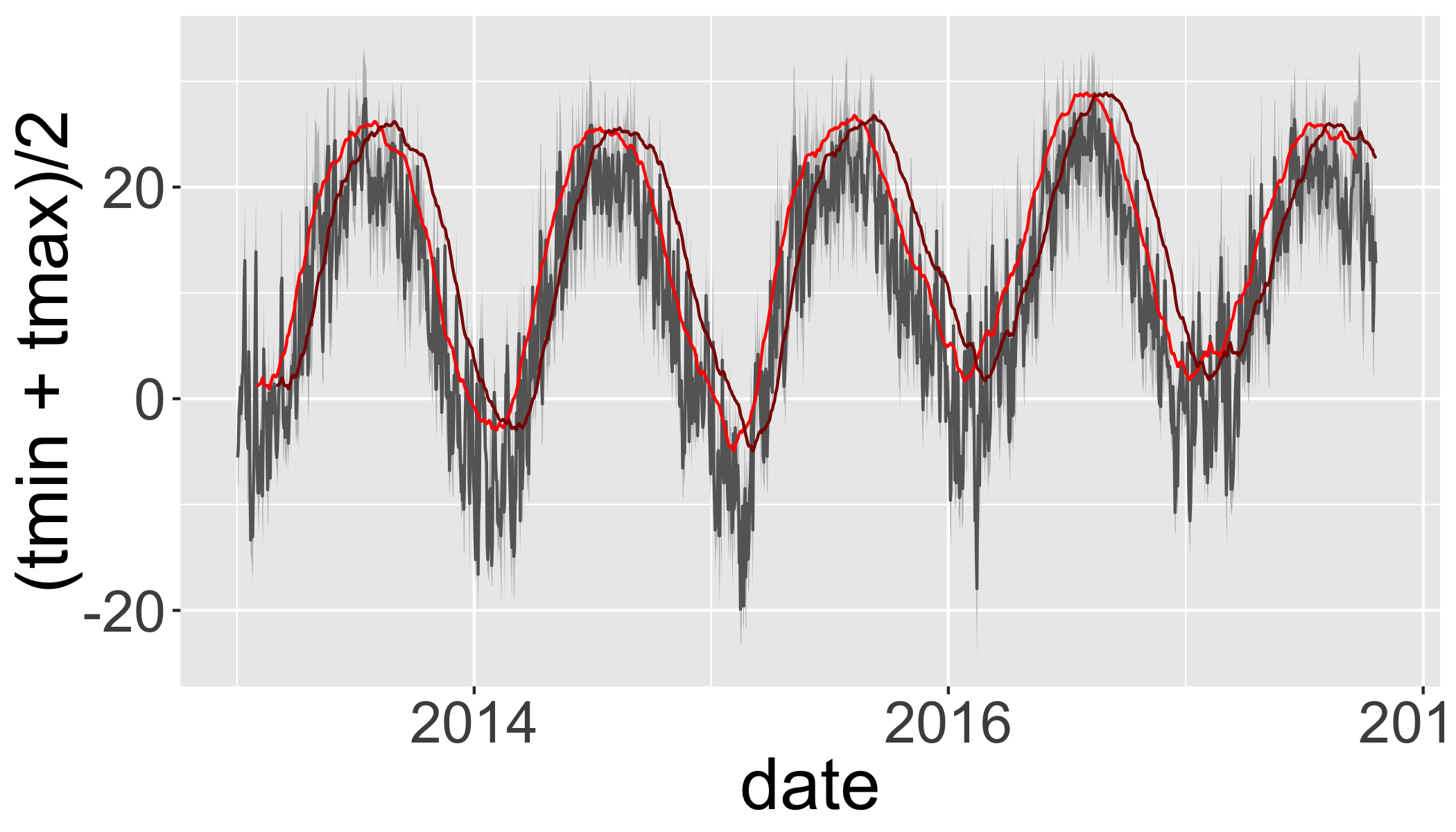
Your Turn
Plot a 30-day rolling “right” aligned sum of precipitation.
tp=d_filtered_recent %>%
arrange(date) %>%
mutate(prcp.30 = rollsum(x = prcp, 30, align = "right", fill = NA))
ggplot(tp,aes(y=prcp,x=date))+
geom_line(aes(y=prcp.30),col="black")+
geom_line(col="red") ## Warning: Removed 40 rows containing missing values (geom_path).## Warning: Removed 11 rows containing missing values (geom_path).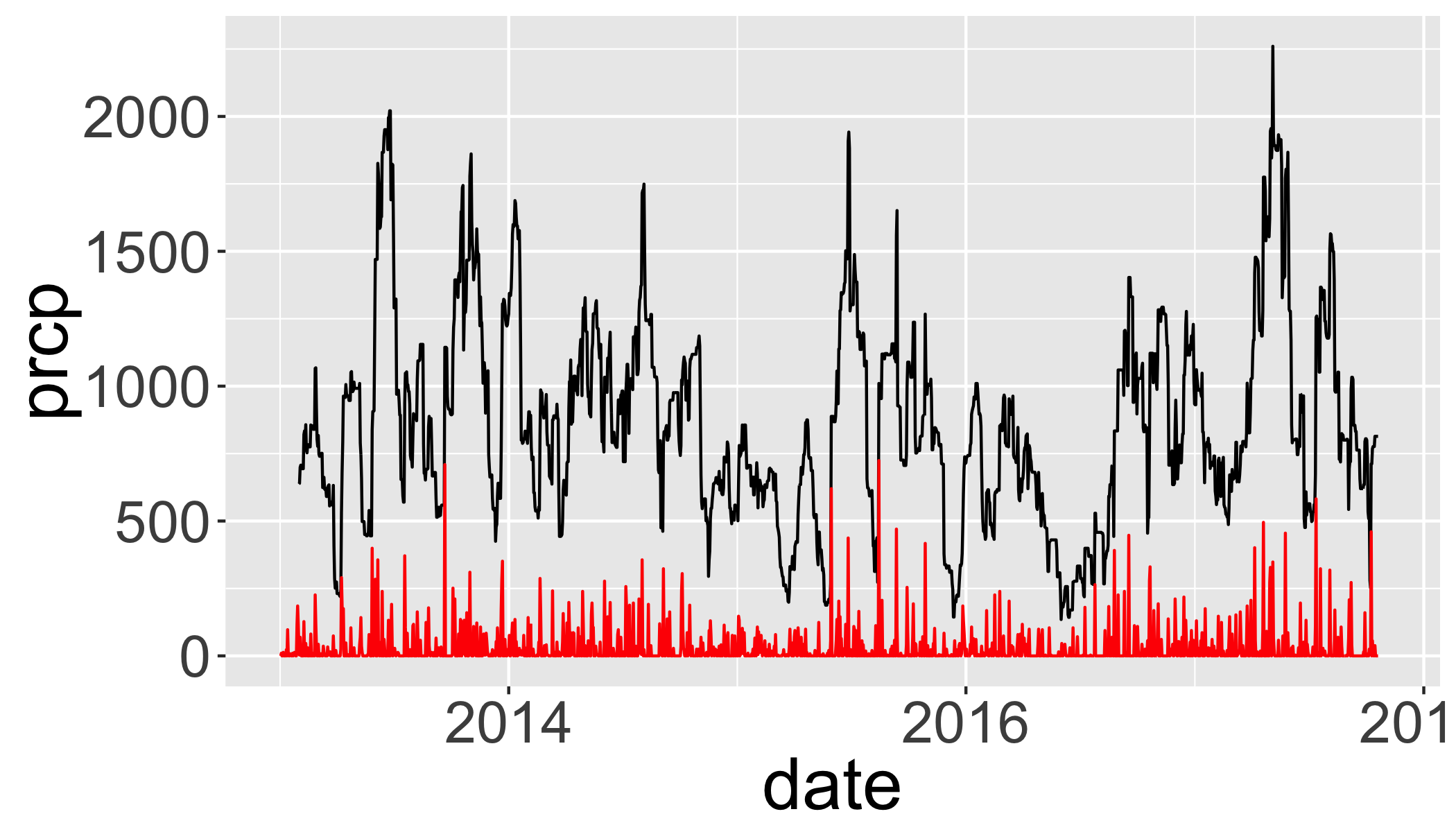
Time Series analysis
Most timeseries functions use the time series class (ts)
tmin.ts=ts(d_filtered_recent$tmin,frequency = 365)Temporal autocorrelation
Values are highly correlated!
ggplot(d_filtered_recent,aes(y=tmin,x=lag(tmin)))+
geom_point()+
geom_abline(intercept=0, slope=1)## Warning: Removed 12 rows containing missing values (geom_point).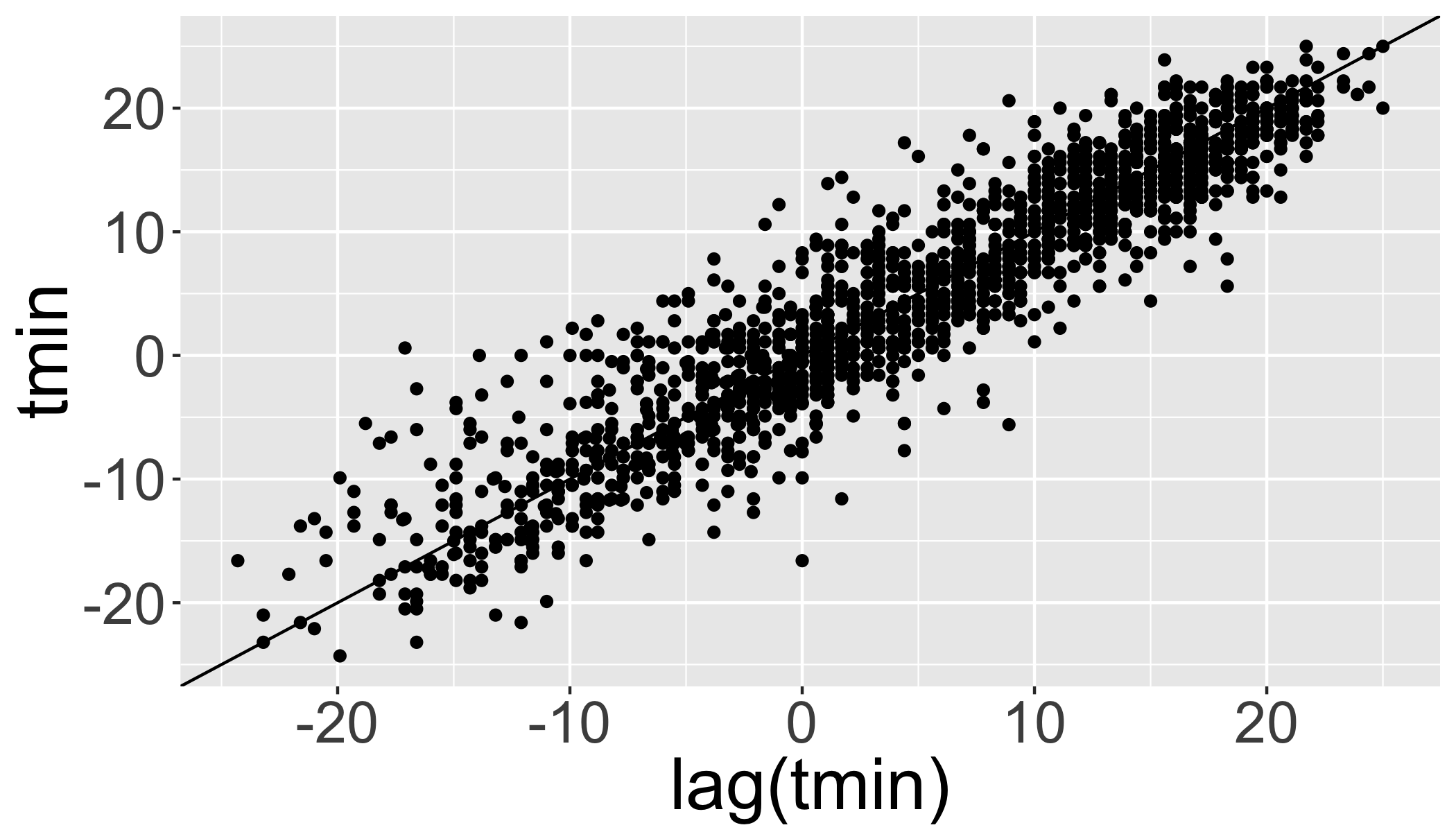
Autocorrelation functions
- autocorrelation x vs. xt − 1 (lag=1)
- partial autocorrelation. x vs. xn after controlling for correlations ∈ t − 1 : n
Autocorrelation
acf(tmin.ts,lag.max = 365*3,na.action = na.exclude )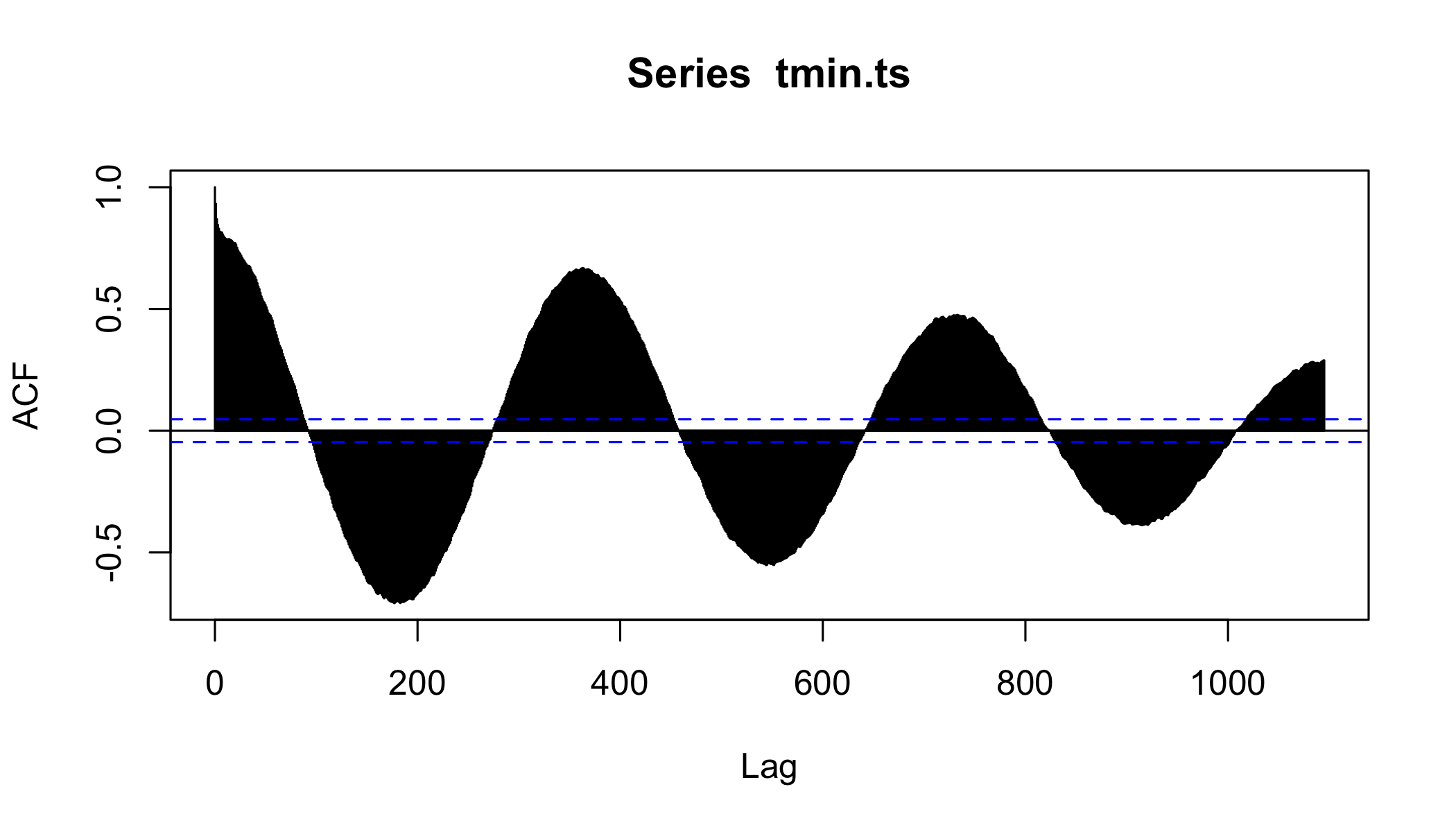
Partial Autocorrelation
pacf(tmin.ts,lag.max = 365*3,na.action = na.exclude )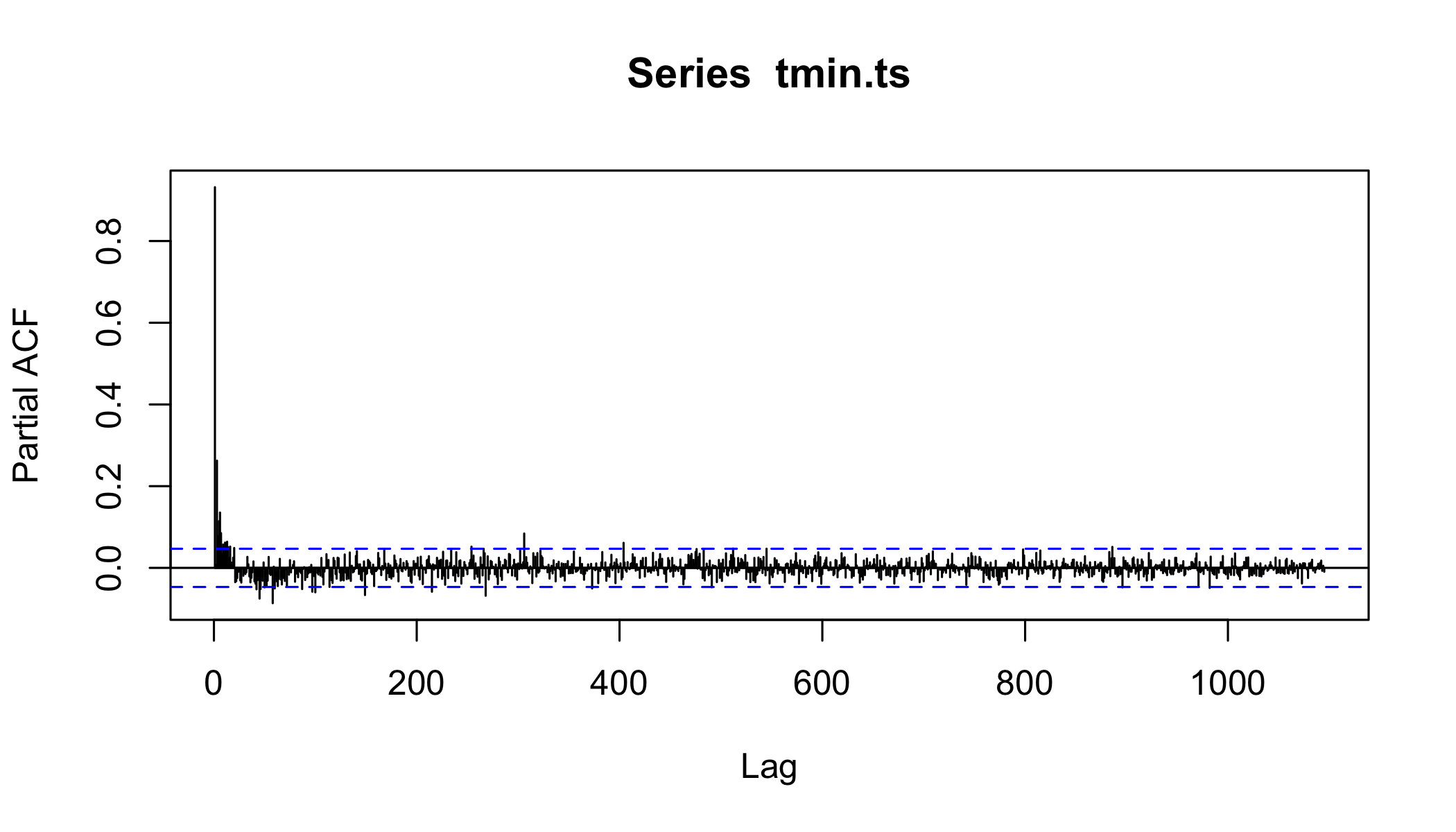
Checking for significant trends
Compute temporal aggregation indices
Group by month, season, year, and decade.
How to convert years into ‘decades’?
1938## [1] 1938round(1938,-1)## [1] 1940floor(1938/10)*10## [1] 1930Calculate seasonal and decadal mean temperatures.
d_filtered2=d_filtered%>%
mutate(month=as.numeric(format(date,"%m")),
year=as.numeric(format(date,"%Y")),
season=ifelse(month%in%c(12,1,2),"Winter",
ifelse(month%in%c(3,4,5),"Spring",
ifelse(month%in%c(6,7,8),"Summer",
ifelse(month%in%c(9,10,11),"Fall",NA)))),
dec=(floor(as.numeric(format(date,"%Y"))/10)*10))
knitr::kable(head(d_filtered2))| id | date | mflag_prcp | mflag_tmax | mflag_tmin | prcp | qflag_prcp | qflag_tmax | qflag_tmin | sflag_prcp | sflag_tmax | sflag_tmin | tmax | tmin | month | year | season | dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USW00014733 | 1938-05-01 | T | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 14.4 | 3.9 | 5 | 1938 | Spring | 1930 | |||||
| USW00014733 | 1938-05-02 | T | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 21.1 | 8.3 | 5 | 1938 | Spring | 1930 | |||||
| USW00014733 | 1938-05-03 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16.7 | 7.2 | 5 | 1938 | Spring | 1930 | ||||||
| USW00014733 | 1938-05-04 | 112 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20.6 | 9.4 | 5 | 1938 | Spring | 1930 | ||||||
| USW00014733 | 1938-05-05 | T | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 31.1 | 10.6 | 5 | 1938 | Spring | 1930 | |||||
| USW00014733 | 1938-05-06 | 64 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19.4 | 7.8 | 5 | 1938 | Spring | 1930 |
Timeseries models
How to assess change? Simple differences?
d_filtered2%>%
mutate(period=ifelse(year<=1976-01-01,"early","late"))%>% #create two time periods before and after 1976
group_by(period)%>% # divide the data into the two groups
summarize(n=n(), # calculate the means between the two periods
tmin=mean(tmin,na.rm=T),
tmax=mean(tmax,na.rm=T),
prcp=mean(prcp,na.rm=T))## # A tibble: 2 x 5
## period n tmin tmax prcp
## <chr> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 early 13394 4.20 13.7 25.1
## 2 late 15645 4.76 13.8 28.4But be careful, there were lots of missing data in the beginning of the record
d_filtered2%>%
group_by(year)%>%
summarize(n=n())%>%
ggplot(aes(x=year,y=n))+
geom_line(col="grey")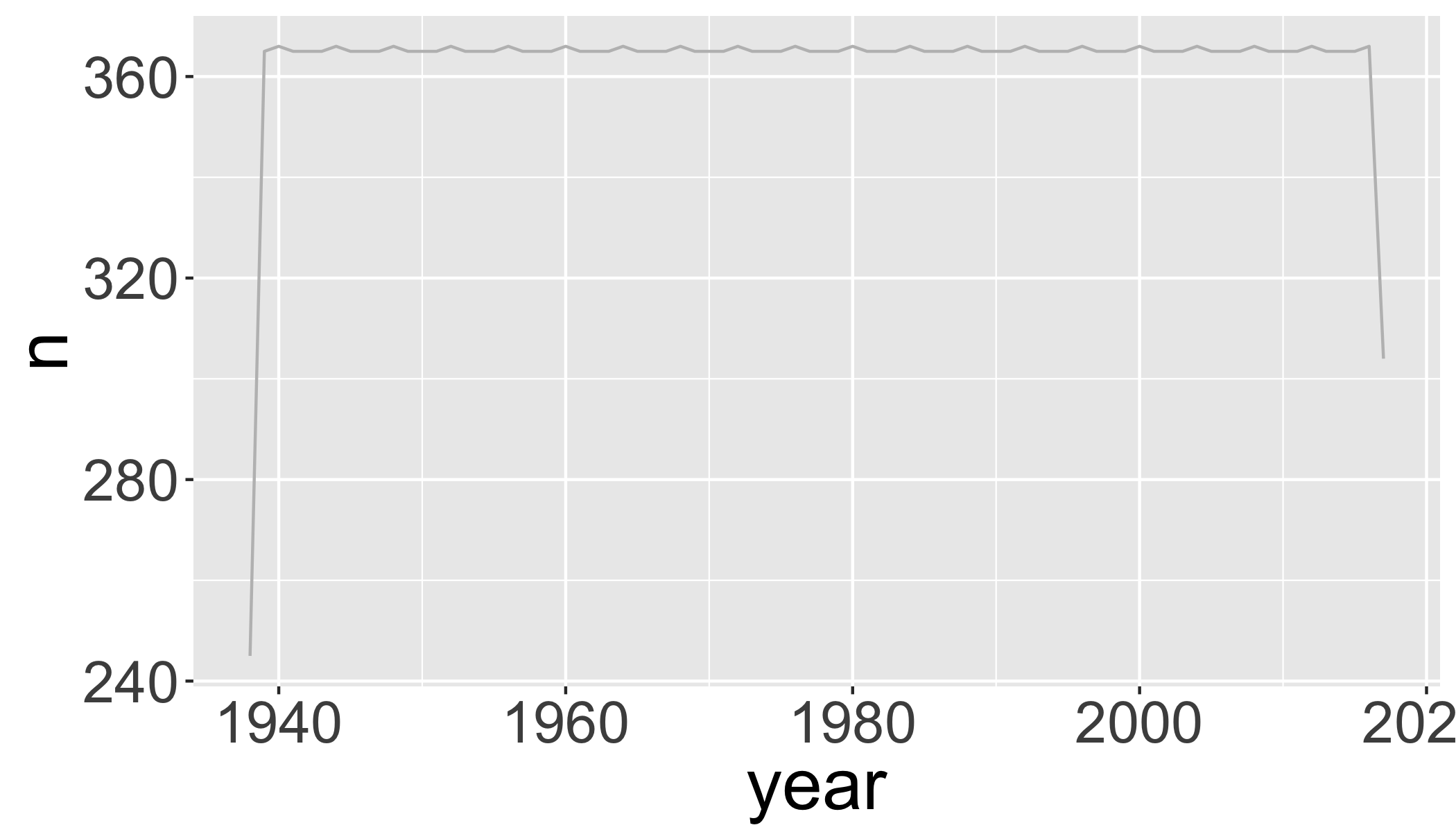
# which years don't have complete data?
d_filtered2%>%
group_by(year)%>%
summarize(n=n())%>%
filter(n<360)## # A tibble: 2 x 2
## year n
## <dbl> <int>
## 1 1938 245
## 2 2017 304Plot 10-year means (excluding years without complete data):
d_filtered2%>%
filter(year>1938, year<2017)%>%
group_by(dec)%>%
summarize(
n=n(),
tmin=mean(tmin,na.rm=T),
tmax=mean(tmax,na.rm=T),
prcp=mean(prcp,na.rm=T)
)%>%
ggplot(aes(x=dec,y=tmax))+
geom_line(col="grey")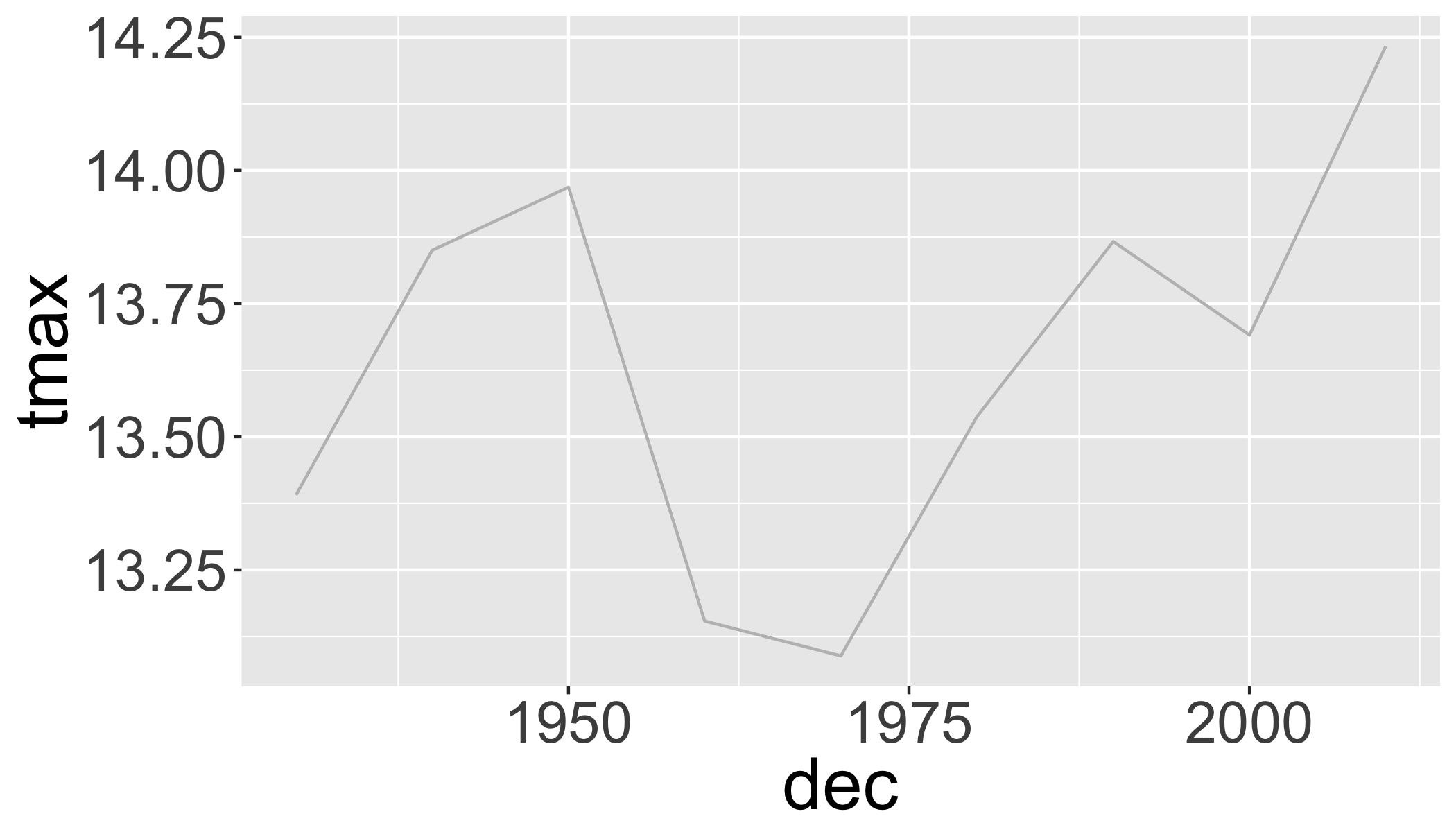
Look for specific events: was 2017 unusually hot in Buffalo, NY?
Let’s compare 2017 with all the previous years in the dataset. First add ‘day of year’ to the data to facilitate showing all years on the same plot.
df=d_filtered2%>%
mutate(doy=as.numeric(format(date,"%j")),
doydate=as.Date(paste("2017-",doy),format="%Y-%j"))Then plot all years (in grey) and add 2017 in red.
ggplot(df,aes(x=doydate,y=tmax,group=year))+
geom_line(col="grey",alpha=.5)+ # plot each year in grey
stat_smooth(aes(group=1),col="black")+ # Add a smooth GAM to estimate the long-term mean
geom_line(data=filter(df,year>2016),col="red")+ # add 2017 in red
scale_x_date(labels = date_format("%b"),date_breaks = "2 months")## `geom_smooth()` using method = 'gam' and formula 'y ~ s(x, bs = "cs")'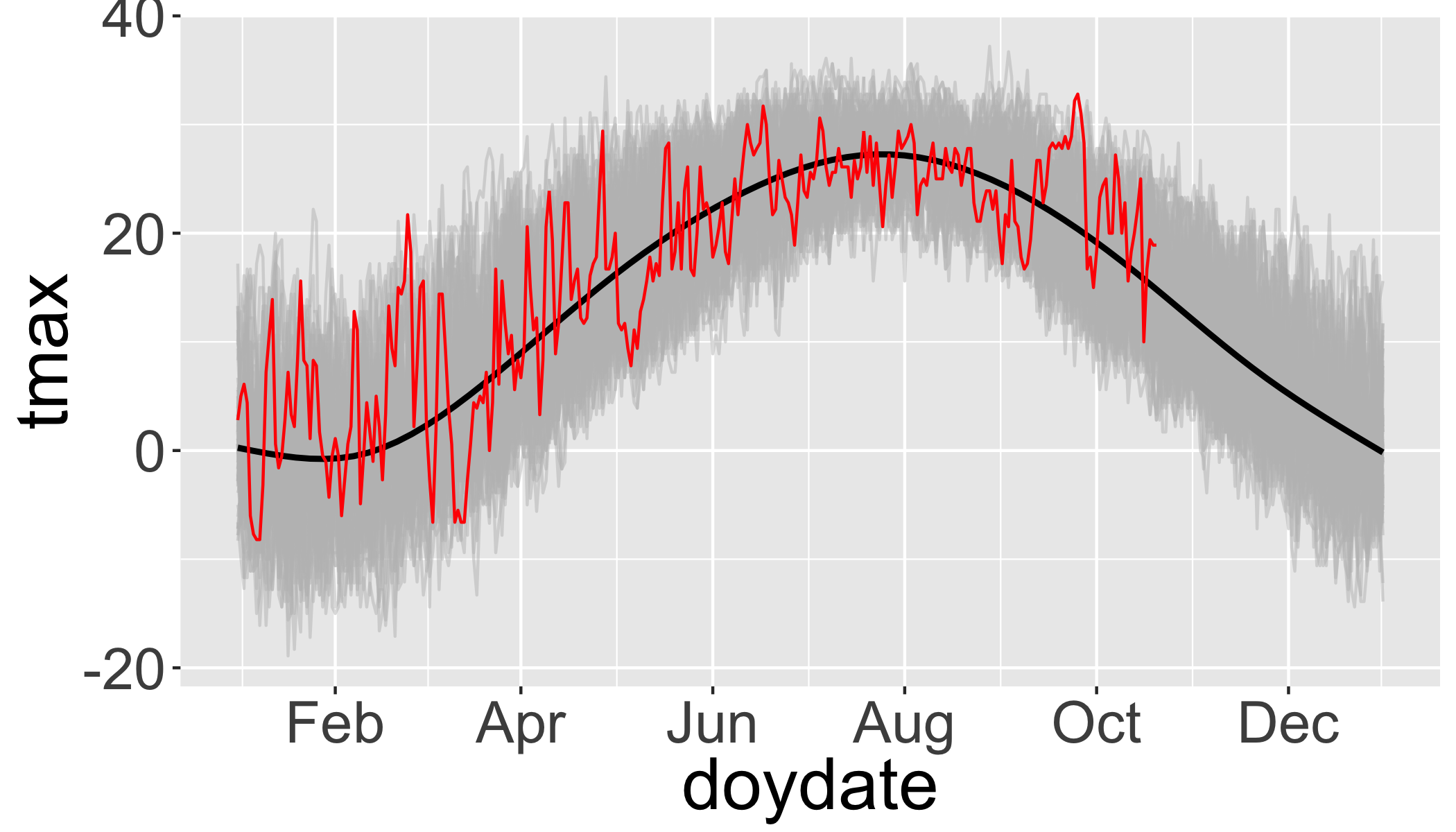
Then ‘zoom’ into just the past few months and add 2017 in red.
ggplot(df,aes(x=doydate,y=tmax,group=year))+
geom_line(col="grey",alpha=.5)+
stat_smooth(aes(group=1),col="black")+
geom_line(data=filter(df,year>2016),col="red")+
scale_x_date(labels = date_format("%b"),date_breaks = "2 months",
lim=c(as.Date("2017-08-01"),as.Date("2017-10-31")))## `geom_smooth()` using method = 'gam' and formula 'y ~ s(x, bs = "cs")'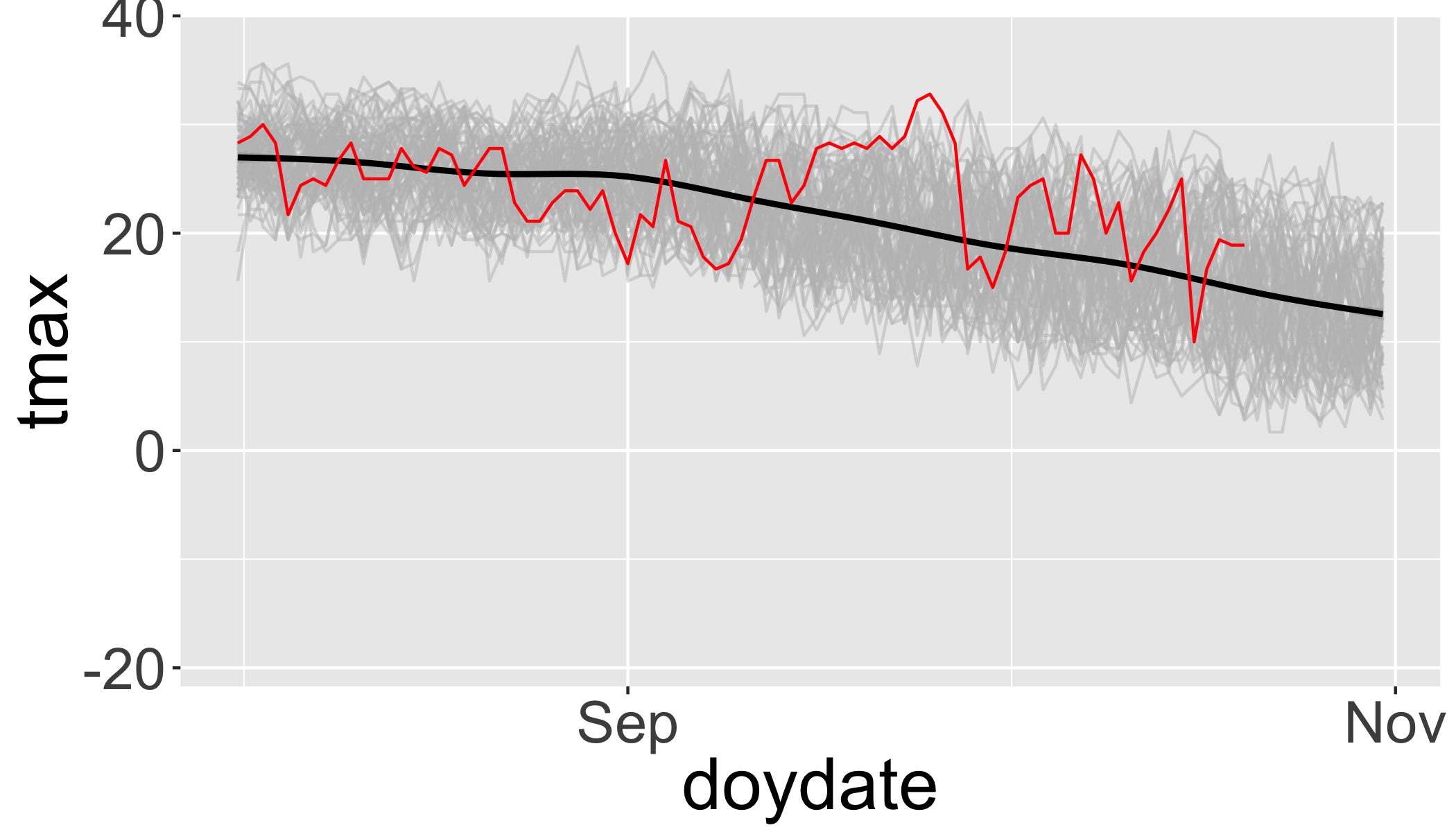
So there was an unusually warm spell in late September.
Summarize by season
seasonal=d_filtered2%>%
group_by(year,season)%>%
summarize(n=n(),
tmin=mean(tmin),
tmax=mean(tmax),
prcp=mean(prcp))%>%
filter(n>75)
ggplot(seasonal,aes(y=tmin,x=year))+
facet_grid(season~.,scales = "free_y")+
stat_smooth(method="lm", se=T)+
geom_line()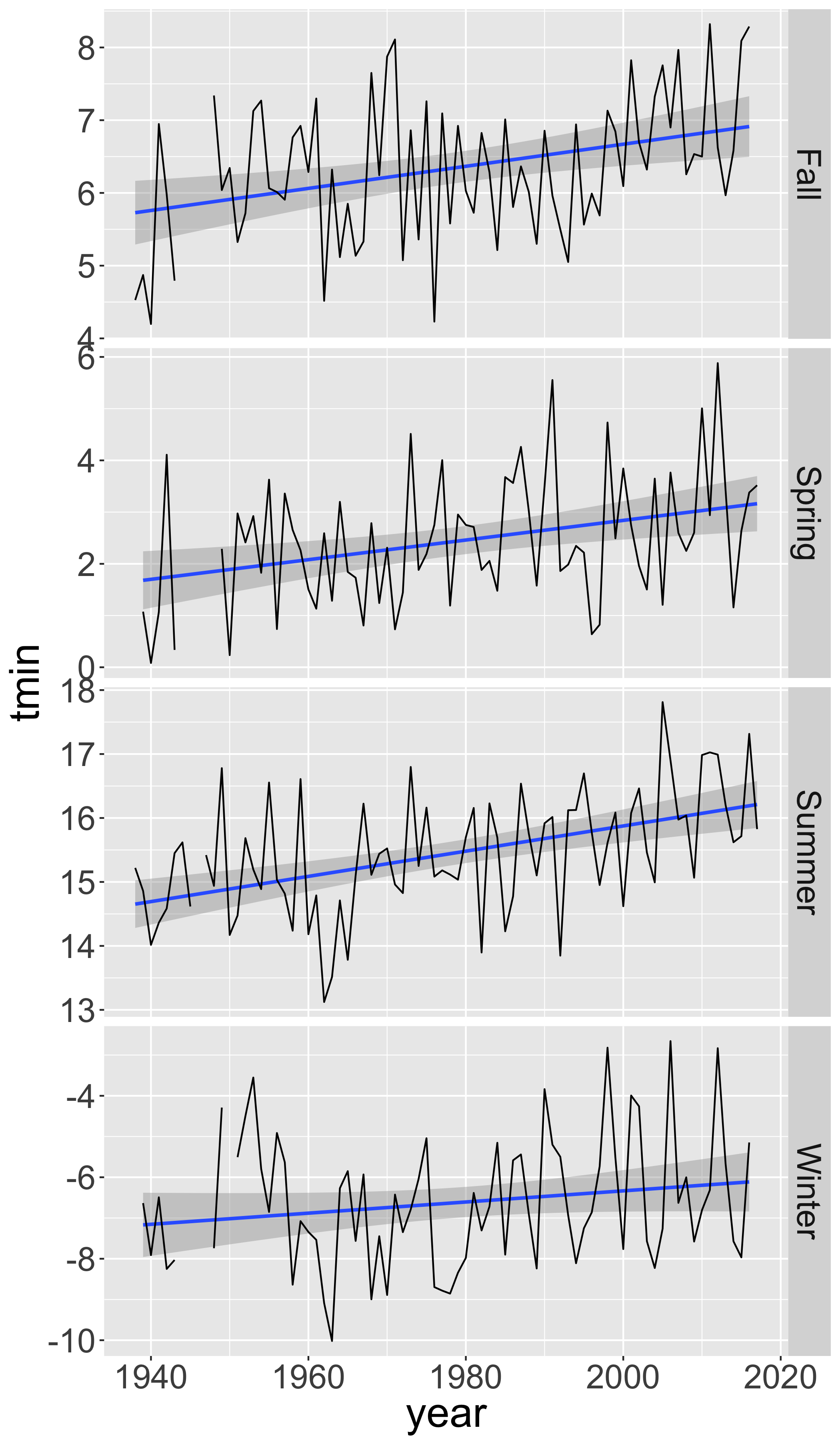
Linear regression of maximum temperature in fall
s1=seasonal%>%
filter(season=="Summer")
ggplot(s1,aes(y=tmin,x=year))+
stat_smooth(method="lm", se=T)+
geom_line()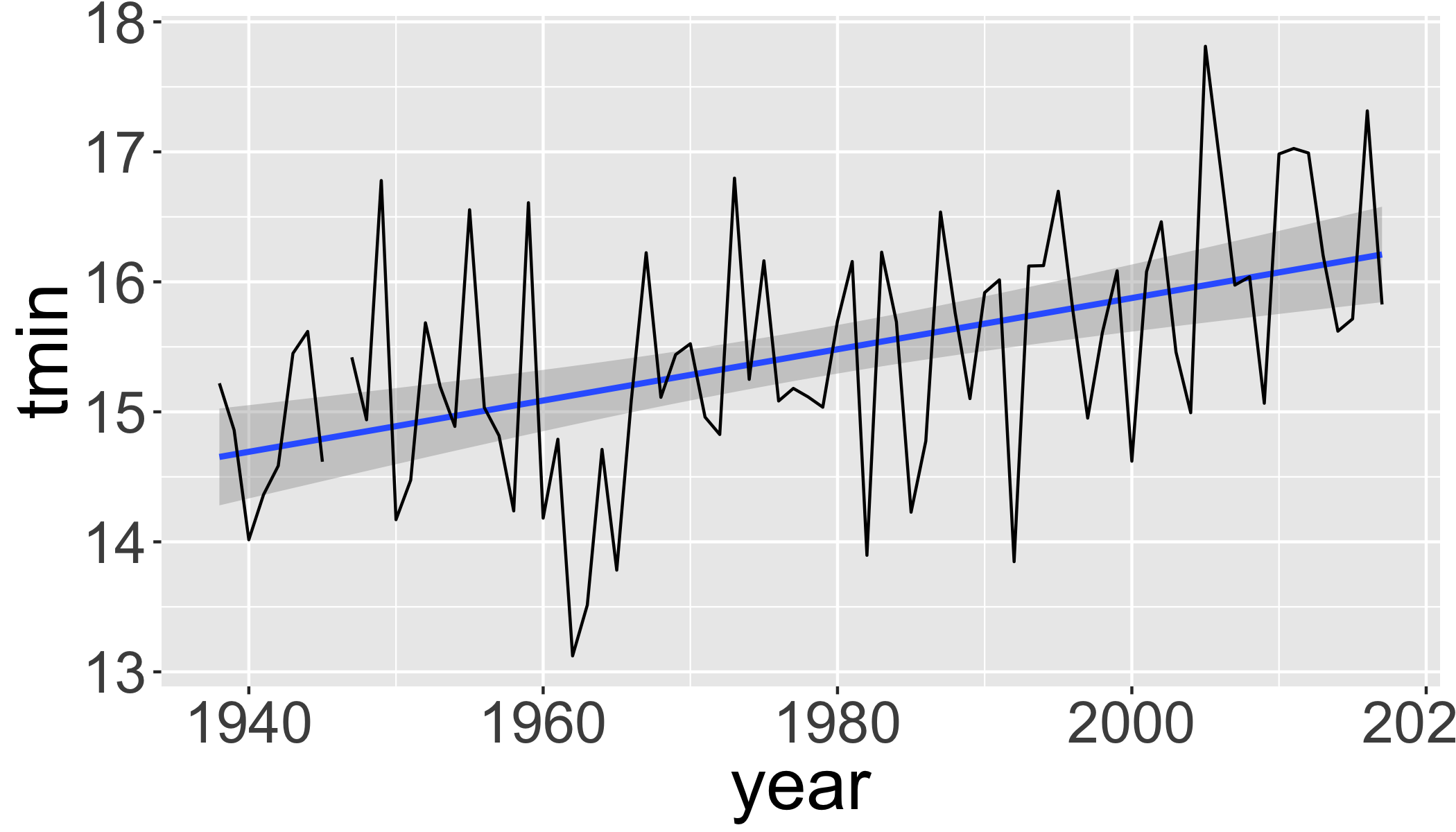
lm1=lm(tmin~year, data=s1)
str(lm1)## List of 13
## $ coefficients : Named num [1:2] -23.551 0.0197
## ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:2] "(Intercept)" "year"
## $ residuals : Named num [1:79] 0.566 0.187 -0.676 -0.349 -0.147 ...
## ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:79] "1" "2" "3" "4" ...
## $ effects : Named num [1:79] -137.232 4.023 -0.752 -0.424 -0.222 ...
## ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:79] "(Intercept)" "year" "" "" ...
## $ rank : int 2
## $ fitted.values: Named num [1:79] 14.7 14.7 14.7 14.7 14.7 ...
## ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:79] "1" "2" "3" "4" ...
## $ assign : int [1:2] 0 1
## $ qr :List of 5
## ..$ qr : num [1:79, 1:2] -8.888 0.113 0.113 0.113 0.113 ...
## .. ..- attr(*, "dimnames")=List of 2
## .. .. ..$ : chr [1:79] "1" "2" "3" "4" ...
## .. .. ..$ : chr [1:2] "(Intercept)" "year"
## .. ..- attr(*, "assign")= int [1:2] 0 1
## ..$ qraux: num [1:2] 1.11 1.17
## ..$ pivot: int [1:2] 1 2
## ..$ tol : num 1e-07
## ..$ rank : int 2
## ..- attr(*, "class")= chr "qr"
## $ df.residual : int 77
## $ na.action :Class 'omit' Named int 9
## .. ..- attr(*, "names")= chr "9"
## $ xlevels : Named list()
## $ call : language lm(formula = tmin ~ year, data = s1)
## $ terms :Classes 'terms', 'formula' language tmin ~ year
## .. ..- attr(*, "variables")= language list(tmin, year)
## .. ..- attr(*, "factors")= int [1:2, 1] 0 1
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "dimnames")=List of 2
## .. .. .. ..$ : chr [1:2] "tmin" "year"
## .. .. .. ..$ : chr "year"
## .. ..- attr(*, "term.labels")= chr "year"
## .. ..- attr(*, "order")= int 1
## .. ..- attr(*, "intercept")= int 1
## .. ..- attr(*, "response")= int 1
## .. ..- attr(*, ".Environment")=<environment: R_GlobalEnv>
## .. ..- attr(*, "predvars")= language list(tmin, year)
## .. ..- attr(*, "dataClasses")= Named chr [1:2] "numeric" "numeric"
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:2] "tmin" "year"
## $ model :'data.frame': 79 obs. of 2 variables:
## ..$ tmin: num [1:79] 15.2 14.9 14 14.4 14.6 ...
## ..$ year: num [1:79] 1938 1939 1940 1941 1942 ...
## ..- attr(*, "terms")=Classes 'terms', 'formula' language tmin ~ year
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "variables")= language list(tmin, year)
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "factors")= int [1:2, 1] 0 1
## .. .. .. ..- attr(*, "dimnames")=List of 2
## .. .. .. .. ..$ : chr [1:2] "tmin" "year"
## .. .. .. .. ..$ : chr "year"
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "term.labels")= chr "year"
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "order")= int 1
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "intercept")= int 1
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "response")= int 1
## .. .. ..- attr(*, ".Environment")=<environment: R_GlobalEnv>
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "predvars")= language list(tmin, year)
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "dataClasses")= Named chr [1:2] "numeric" "numeric"
## .. .. .. ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:2] "tmin" "year"
## ..- attr(*, "na.action")=Class 'omit' Named int 9
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "names")= chr "9"
## - attr(*, "class")= chr "lm"summary(lm1)##
## Call:
## lm(formula = tmin ~ year, data = s1)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.00360 -0.45550 -0.02385 0.57754 1.90919
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) -23.551009 8.042522 -2.928 0.00448 **
## year 0.019713 0.004066 4.848 6.33e-06 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 0.8298 on 77 degrees of freedom
## (1 observation deleted due to missingness)
## Multiple R-squared: 0.2339, Adjusted R-squared: 0.2239
## F-statistic: 23.51 on 1 and 77 DF, p-value: 6.333e-06You can extract values of interest by looking at the structure of the object.
str(summary(lm1))## List of 12
## $ call : language lm(formula = tmin ~ year, data = s1)
## $ terms :Classes 'terms', 'formula' language tmin ~ year
## .. ..- attr(*, "variables")= language list(tmin, year)
## .. ..- attr(*, "factors")= int [1:2, 1] 0 1
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "dimnames")=List of 2
## .. .. .. ..$ : chr [1:2] "tmin" "year"
## .. .. .. ..$ : chr "year"
## .. ..- attr(*, "term.labels")= chr "year"
## .. ..- attr(*, "order")= int 1
## .. ..- attr(*, "intercept")= int 1
## .. ..- attr(*, "response")= int 1
## .. ..- attr(*, ".Environment")=<environment: R_GlobalEnv>
## .. ..- attr(*, "predvars")= language list(tmin, year)
## .. ..- attr(*, "dataClasses")= Named chr [1:2] "numeric" "numeric"
## .. .. ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:2] "tmin" "year"
## $ residuals : Named num [1:79] 0.566 0.187 -0.676 -0.349 -0.147 ...
## ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:79] "1" "2" "3" "4" ...
## $ coefficients : num [1:2, 1:4] -23.55101 0.01971 8.04252 0.00407 -2.92831 ...
## ..- attr(*, "dimnames")=List of 2
## .. ..$ : chr [1:2] "(Intercept)" "year"
## .. ..$ : chr [1:4] "Estimate" "Std. Error" "t value" "Pr(>|t|)"
## $ aliased : Named logi [1:2] FALSE FALSE
## ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:2] "(Intercept)" "year"
## $ sigma : num 0.83
## $ df : int [1:3] 2 77 2
## $ r.squared : num 0.234
## $ adj.r.squared: num 0.224
## $ fstatistic : Named num [1:3] 23.5 1 77
## ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:3] "value" "numdf" "dendf"
## $ cov.unscaled : num [1:2, 1:2] 93.928528 -0.047483 -0.047483 0.000024
## ..- attr(*, "dimnames")=List of 2
## .. ..$ : chr [1:2] "(Intercept)" "year"
## .. ..$ : chr [1:2] "(Intercept)" "year"
## $ na.action :Class 'omit' Named int 9
## .. ..- attr(*, "names")= chr "9"
## - attr(*, "class")= chr "summary.lm"summary(lm1)$r.squared## [1] 0.2338852Print a summary table:
tidy(lm1)## # A tibble: 2 x 5
## term estimate std.error statistic p.value
## <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 (Intercept) -23.6 8.04 -2.93 0.00448
## 2 year 0.0197 0.00407 4.85 0.00000633Autoregressive models
See Time Series Analysis Task View for summary of available packages/models.
- Moving average (MA) models
- autoregressive (AR) models
- autoregressive moving average (ARMA) models
- frequency analysis
- Many, many more…
Climate Metrics
Climdex indices
Format data for climdex
library(PCICt)
## Parse the dates into PCICt.
pc.dates <- as.PCICt(as.POSIXct(d_filtered$date),cal="gregorian")Generate the climdex object
library(climdex.pcic)
ci <- climdexInput.raw(
tmax=d_filtered$tmax,
tmin=d_filtered$tmin,
prec=d_filtered$prcp,
pc.dates,pc.dates,pc.dates,
base.range=c(1971, 2000))
years=as.numeric(as.character(unique(ci@date.factors$annual)))Cumulative dry days
cdd= climdex.cdd(ci, spells.can.span.years = TRUE)
plot(cdd~years,type="l")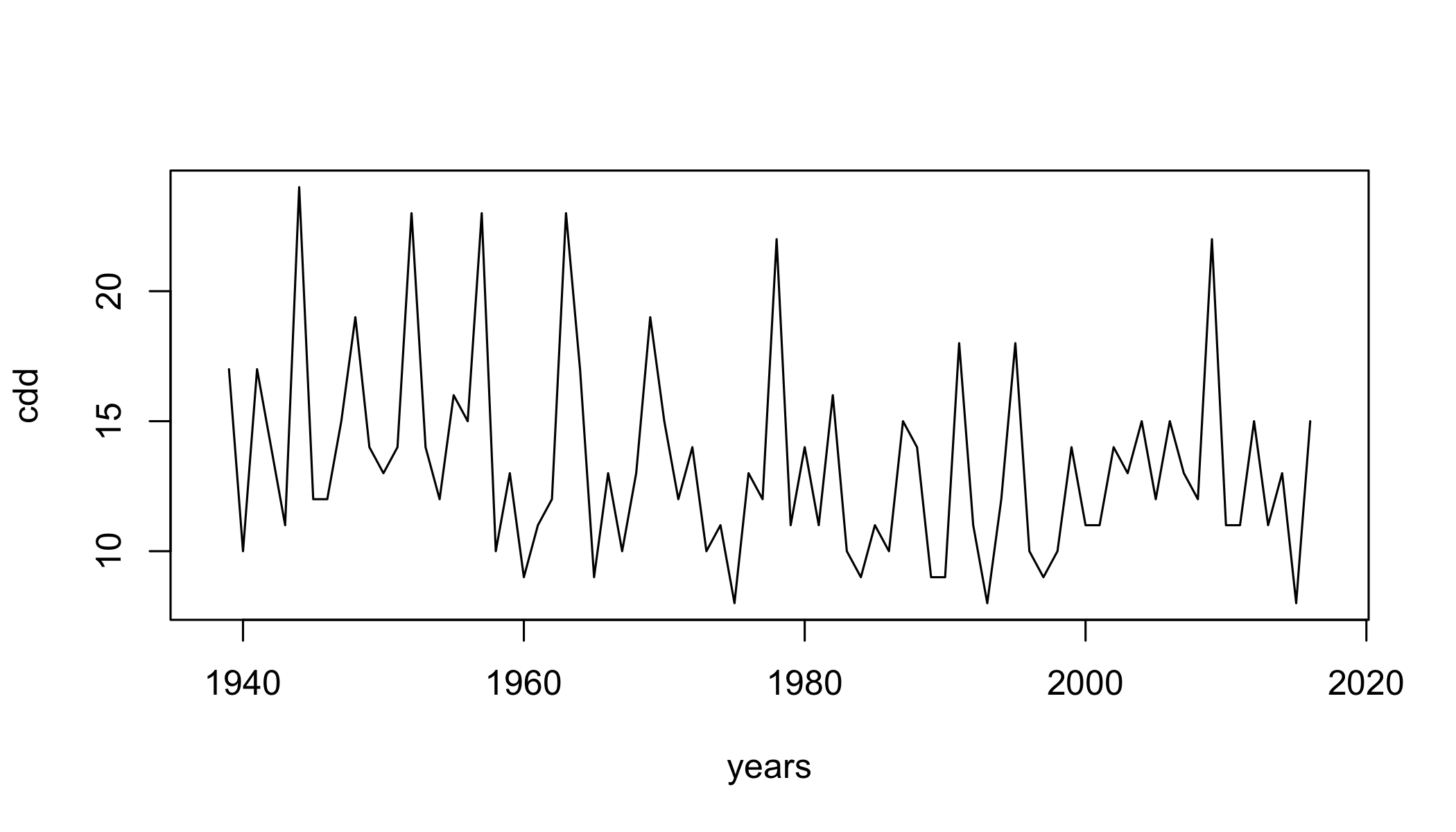
Diurnal Temperature Range
dtr=climdex.dtr(ci, freq = c("annual"))
plot(dtr~years,type="l")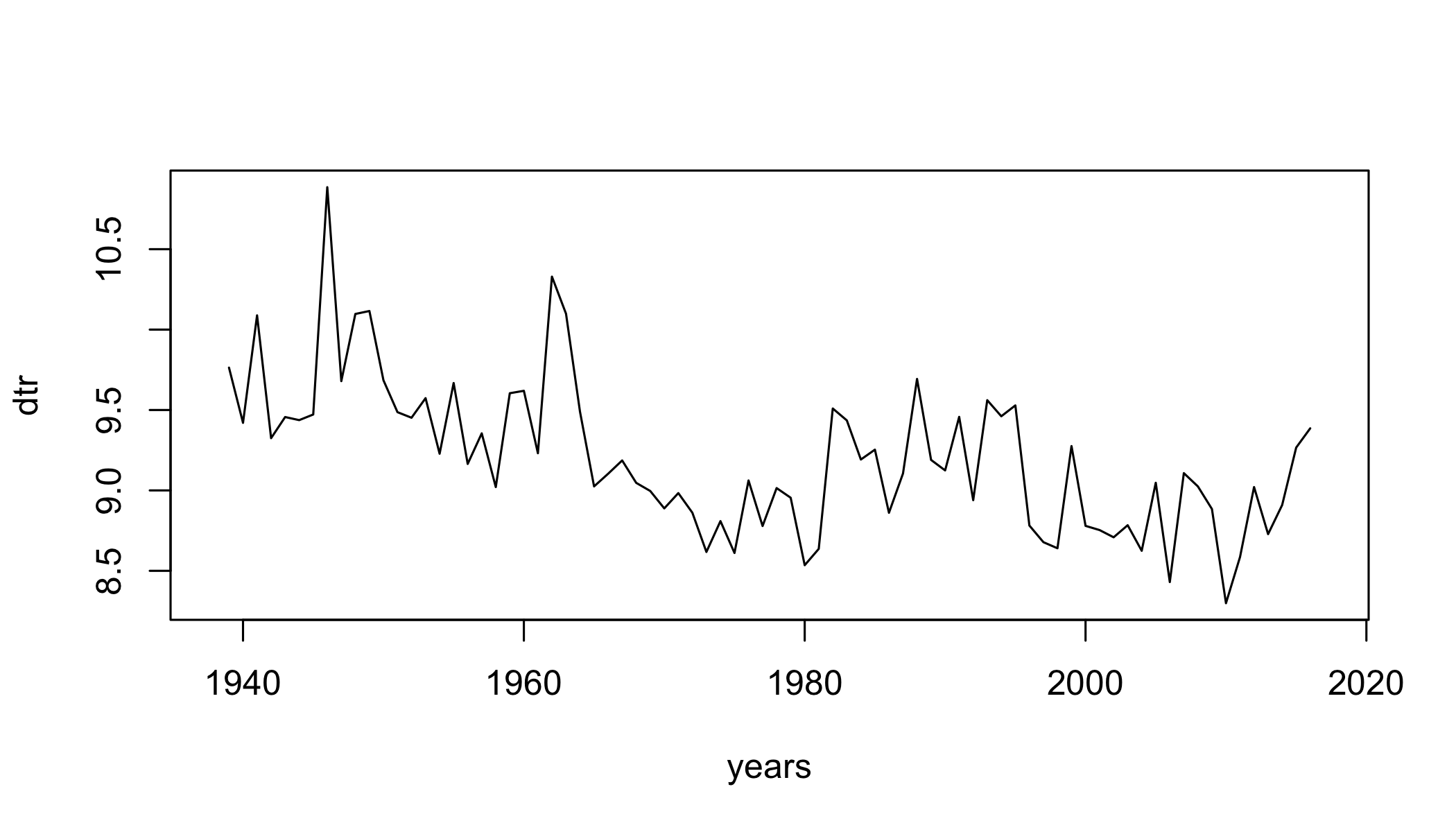
Frost Days
fd=climdex.fd(ci)
plot(fd~years,type="l")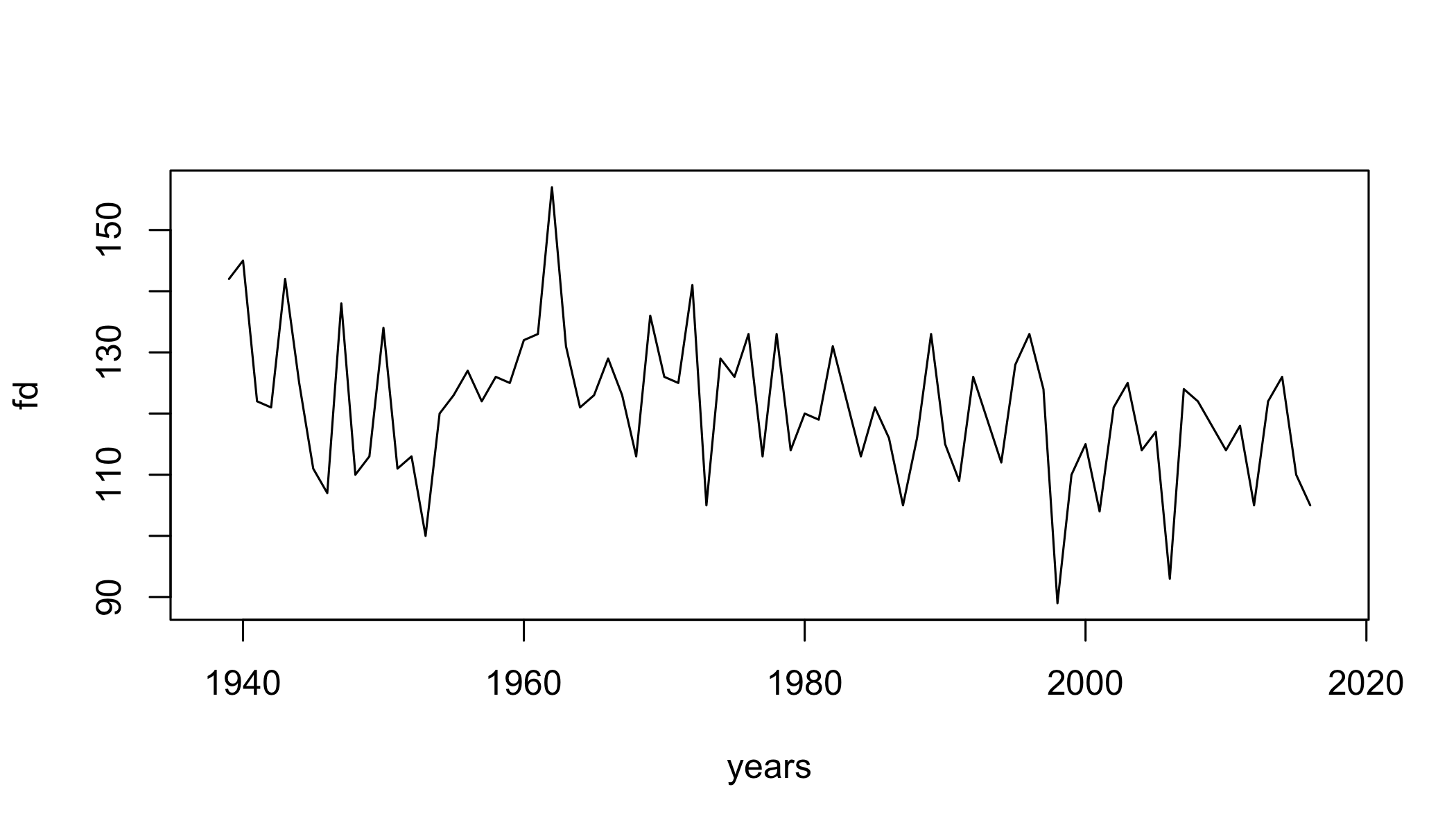
Your Turn
See all available indices with:
climdex.get.available.indices(ci)## [1] "climdex.su" "climdex.id" "climdex.txx"
## [4] "climdex.txn" "climdex.tx10p" "climdex.tx90p"
## [7] "climdex.wsdi" "climdex.fd" "climdex.tr"
## [10] "climdex.tnx" "climdex.tnn" "climdex.tn10p"
## [13] "climdex.tn90p" "climdex.csdi" "climdex.rx1day"
## [16] "climdex.rx5day" "climdex.sdii" "climdex.r10mm"
## [19] "climdex.r20mm" "climdex.rnnmm" "climdex.cdd"
## [22] "climdex.cwd" "climdex.r95ptot" "climdex.r99ptot"
## [25] "climdex.prcptot" "climdex.gsl" "climdex.dtr"Select 3 indices, calculate them, and plot the timeseries.
r10mm=climdex.r10mm(ci)
plot(r10mm~years,type="l")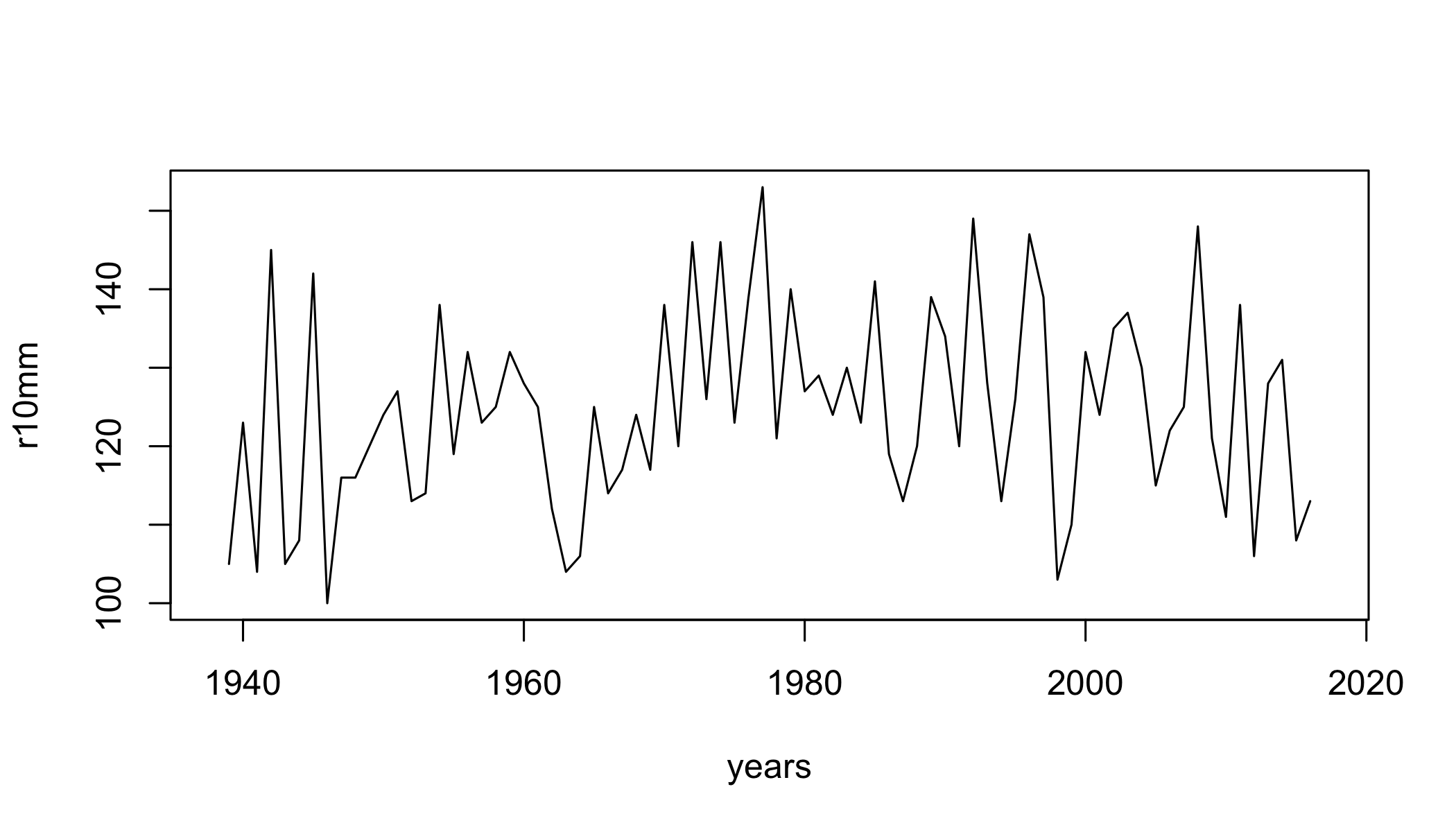
prcptot=climdex.prcptot(ci)
plot(prcptot~years,type="l")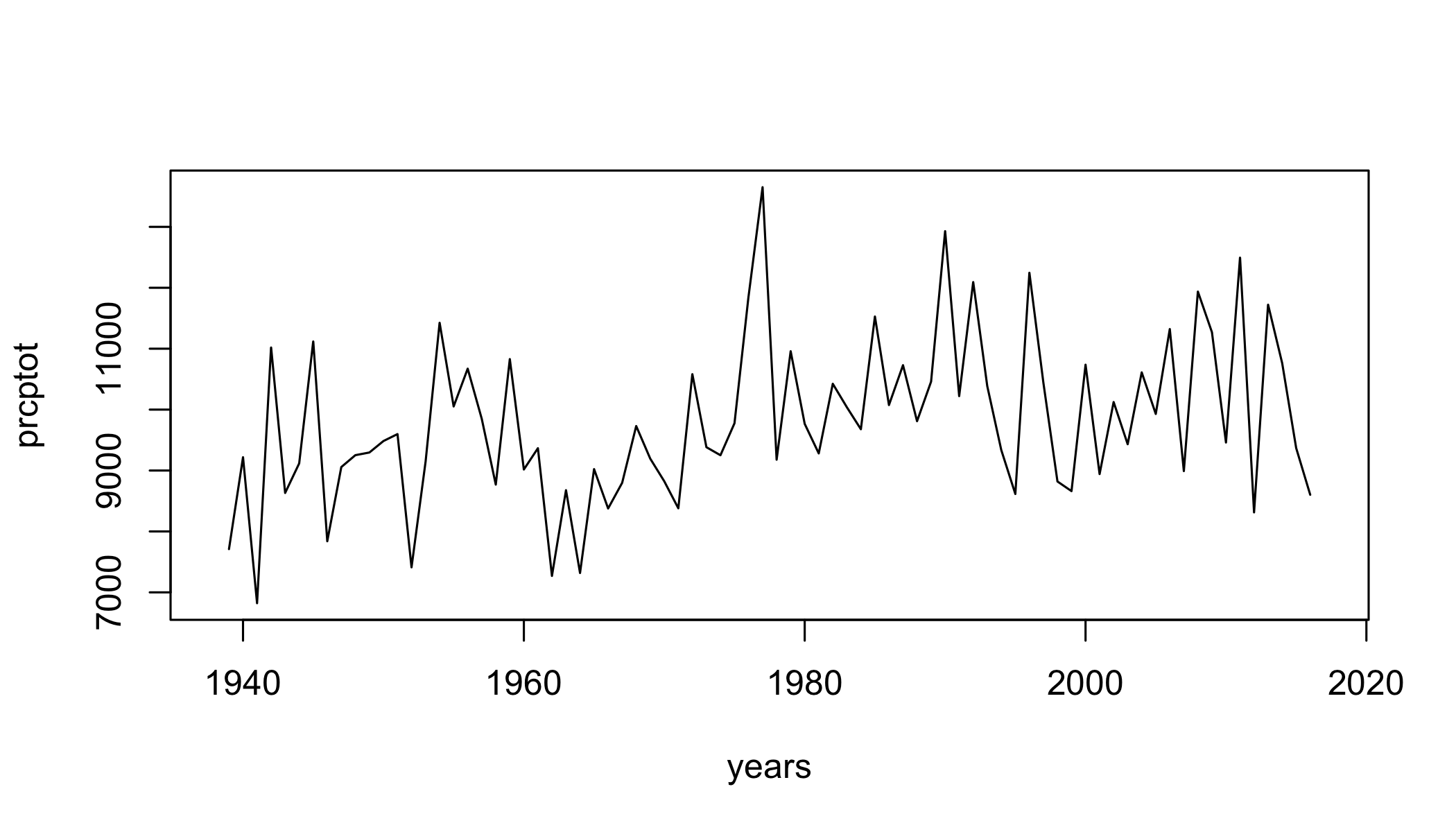
gsl=climdex.gsl(ci)
plot(gsl~years,type="l")