Version Control
Keeping up
DataCamp
Advantages of DataCamp
- Slick dynamic interface
- Lots of help available
- Can provide hints (reducing XP points)
- Easy to earn extra XP points with ‘practice’
- Free access to their ‘premium’ content (typically $29/month)
- Additional ‘Certification’ that you can list on LinkedIn, CV, etc.
Data Camp Screenshot
Proposed course restructure
- DataCamp chapter ‘assignments’ instead of homeworks
- Less talking / lecturing material in class
- More time in class to work on group case studies, ask questions, etc.
Version Control: Keeping track of your files.
“The goal of reproducible research is to tie specific instructions to data analysis and experimental data so that scholarship can be recreated, better understood, and verified.”
Max Kuhn, CRAN Task View: Reproducible Research
Philosphy
Remember, the data and code are real, the products (tables, figures) are ephemeral…
Our work exists on a spectrum of reproducibility
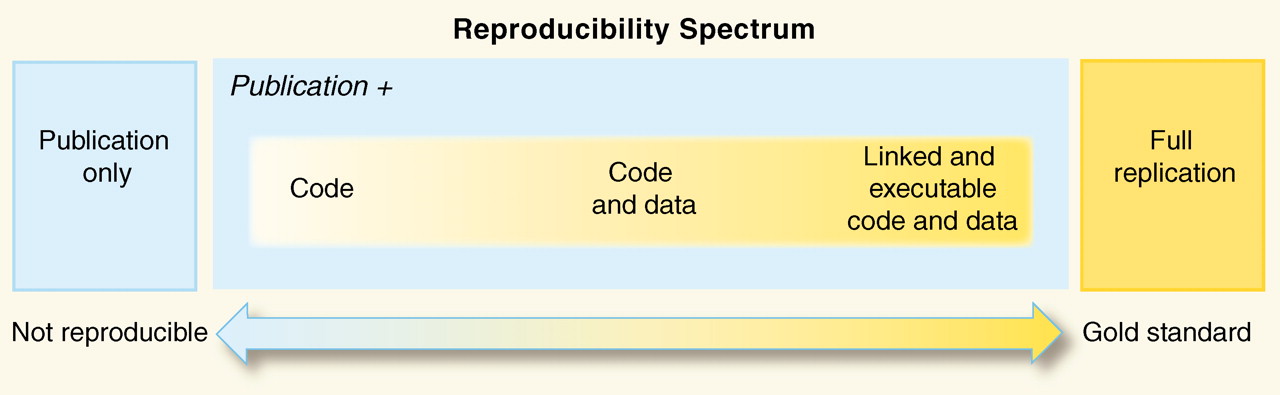
Peng 2011, Science 334(6060) pp. 1226-1227
The Claerbout Principle
“An article about computational result is advertising, not scholarship. The actual scholarship is the full software environment, code and data, that produced the result.”
Claerbout and Karrenbach, Proceedings of the 62nd Annual International Meeting of the Society of Exploration Geophysics. 1992
Tracking changes with version control
Payoffs
- Eases collaboration
- Can track changes in any file type (plain text)
- Can revert file to any point in its tracked history
Costs
- Learning curve
Git
- Strong support for non-linear development: Rapid branching and merging, specific tools for visualizing and navigating a non-linear development history.
- Distributed development: No central server needed, each user has a full copy
- Efficient handling of large projects: Designed to manage the Linux OS
- Cryptographic authentication of history: The ID of a particular version depends uponthe complete history. Once published, it is not possible to change the old versions without it being noticed.
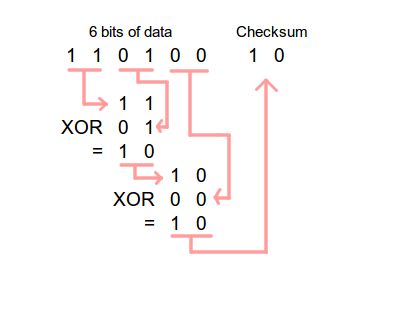
Git Has Integrity
Everything checksummed before storage and then referred by checksum.
It’s impossible to change the contents of any file or directory without Git knowing. You can’t lose information in transit or get file corruption without Git being able to detect it.
Checksum
A way of reducing digital information to a unique ID:
A 40-character hexadecimal SHA-1 hash: 24b9da6552252987aa493b52f8696cd6d3b00373
Git doesn’t care about filenames, extensions, etc. It’s the information that matters…
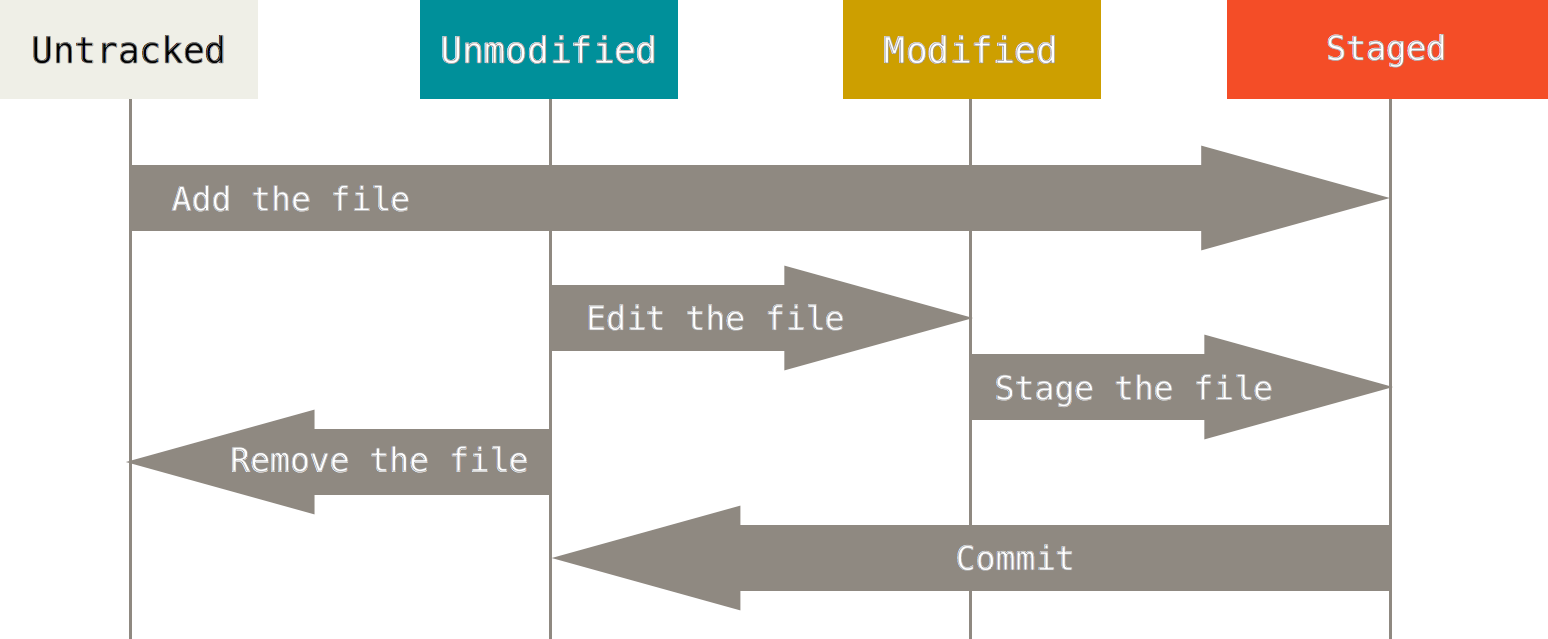
The 3 states of files
staged, modified, committed
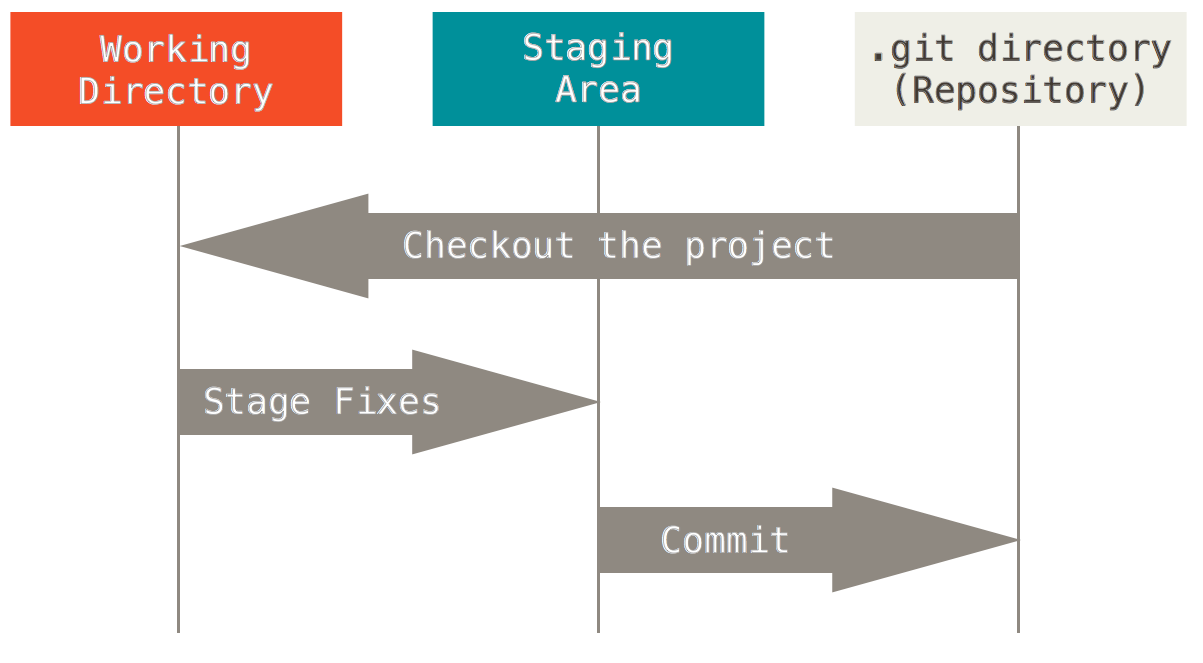
The important stuff is hidden in the .git folder.
Github
Think of Github as a…
- Server to back up your files
- Website to share your files
- Method to track changes to your files
- Platform to collaboratively develop code
- Social media to show off your coding wizardry
Example: course website managed with GitHub
Github Alternatives
Host your own server or use another private company, such as BitBucket.
Git use in this course
- Set up class repository
- Make changes (edit the code)
- Save those changes as you go (ctrl-S)
- Stage changes (get ready to commit them)
- Commit changes at various milestones (like the end of the day or when you finish something)
- Push those changes to github (back them up)
- repeat
Function of Git Repository for this course
- Force you to learn git (a little)
- Force you to organize
- Prepare you for collaborative coding
- Allow me to see your in-class participation
Commit to GitHub from within RStudio
Basic Steps
- Edit: make changes to a file in the repository you cloned above
- Stage: tell git which changes you want to commit
- Commit (with a message)
- Push: send the updated files to GitHub
Edit
Git tracks all changes to files inside a repository.
Stage
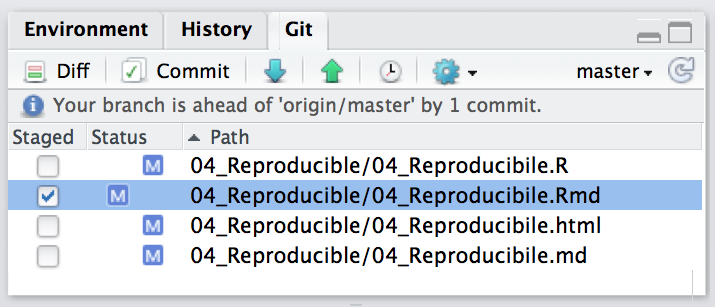
Select which changed files (added, deleted, or edited) you want to commit.
Commit
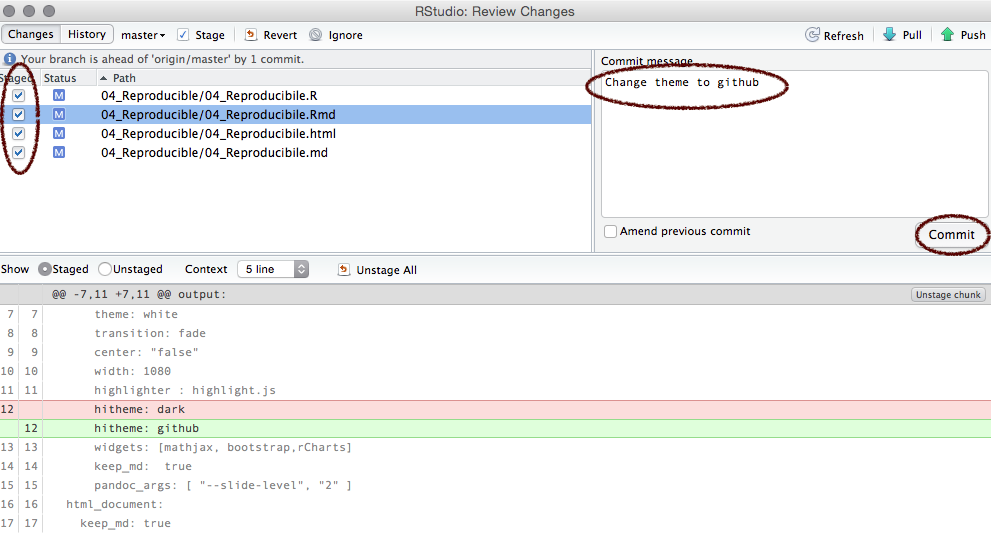
Add a commit message and click commit.
Sync (push)
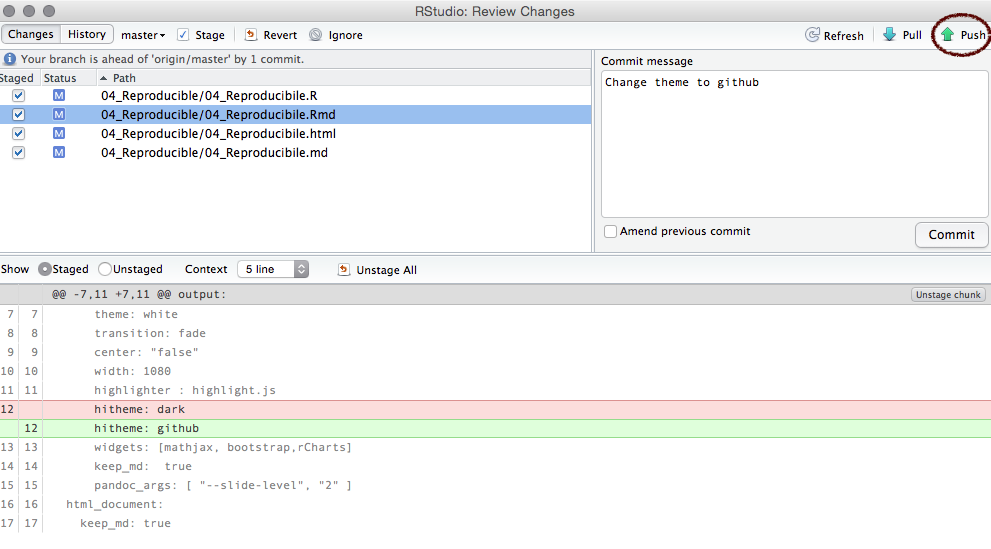
Click the green arrow to sync with GitHub.
Git File Lifecycle
And much more!
Git has many, many more features…
Let’s do it!
Task 2
More advanced Git
Git command line from RStudio
RStudio has limited functionality.
Git help
$ git help <verb>
$ git <verb> --help
$ man git-<verb>For example, you can get the manpage help for the config command by running git help config
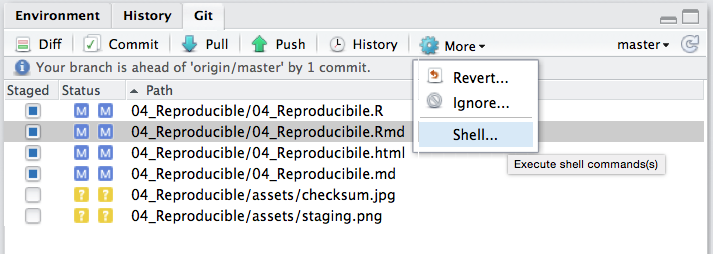
Git status
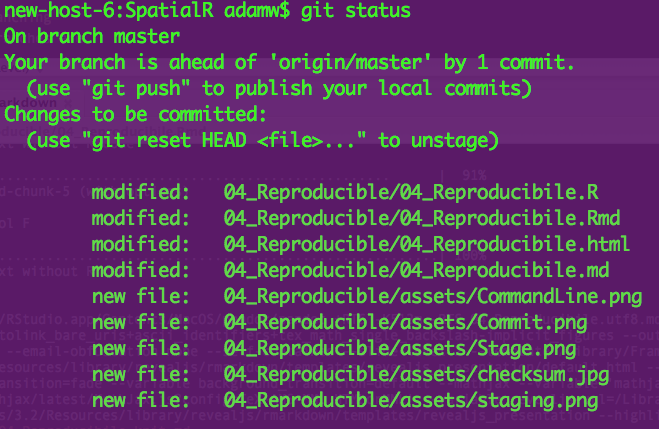
Similar to info in git tab in RStudio
Git config
git config shows you all the git configuration settings:
user.emailremote.origin.url(e.g. to connect to GitHub)
Branching
Branches used to develop features isolated from each other. 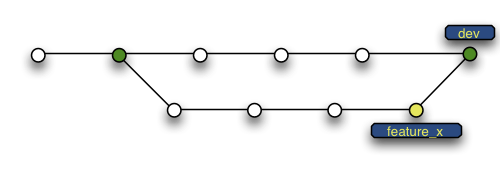
Default: master branch. Use other branches for development/collaboration and merge them back upon completion.
Basic Branching
$ git checkout -b devel # create new branch and switch to it
$ git checkout master #switch back to master
$ git merge devel #merge in changes from devel branchBut we won’t do much with branching in this course…
Git can do far more!
Check out the (free) book ProGIT

Or the cheatsheet.
Colophon
Slides adapted from Dr. Çetinkaya-Rundel and Ben Marwick’s presentation to the UW Center for Statistics and Social Sciences (12 March 2014) (OrcID)
